Engage the Senior Executive
The Engage the Senior Executive module of the CUSP Toolkit focuses on the role and responsibilities of the senior executive within the CUSP team. Engaging a senior executive to partner with a unit will bridge the gap between senior management and frontline providers and will facilitate a system-level perspective on quality and safety challenges that exist at the unit level.
Contents
- Slide 1. Cover Slide
- Slide 2: Learning Objectives
- Slide 3: Using the 4 E's for Technical and Adaptive Work1
- Slide 4: Senior Executive’s Characteristics
- Slide 5: The Senior Executive’s Characteristics
- Slide 6: Senior Executive’s Responsibilities
- Slide 7: The Senior Executive’s Roles and Responsibilities
- Slide 8: Emphasizes Effective Communication
- Slide 9: Meets Monthly With the CUSP Team
- Slide 10: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change
- Slide 11: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change
- Slide 12: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change
- Slide 13: Collaborates To Develop and Implement a Plan Addressing Safety Issues
- Slide 14: The Senior Executive’s Role on the Team
- Slide 15: Holds Staff Accountable for Reducing Patient Harm
- Slide 16: The Challenges of Partnering With a Senior Executive
- Slide 17: How to Engage Your Senior Executive and Develop Shared Accountability for the Work
- Slide 18: Exercise
- Slide 19: Engage the Senior Executive: What the Team Needs to Do
- Slide 20: Summary
- Slide 21: CUSP Tools
- Slide 22: References
Note: Slide content is presented below each of the images.
Slide 1: Cover Slide
Image: (CUSP Toolkit logo)
Slide 2: Learning Objectives
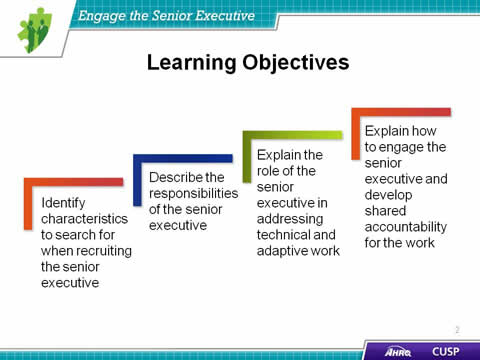
- Identify characteristics to search for when recruiting the senior executive.
- Describe the responsibilities the senior executive must take on.
- Explain the role of the senior executive in addressing technical and adaptive work.
- Explain how to engage the senior executive and develop shared accountability for the work.
Slide 3: Using the 4 E’s for Technical and Adaptive Work1
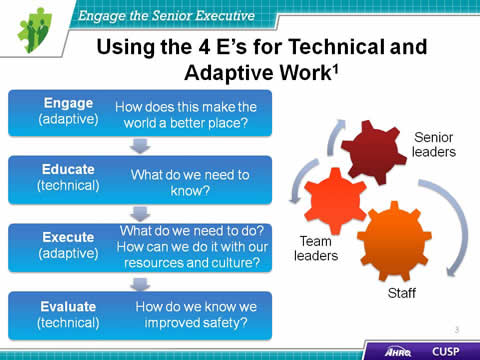
- Engage (adaptive)
- How does this make the world a better place?
- Educate (technical)
- What do we need to know?
- Execute (adaptive)
- What do we need to do? How can we do it with our resources and culture?
- Evaluate (technical)
- How do we know we improved safety?
Slide 4: Senior Executive’s Characteristics

- Vice president level or higher when possible.
- Actively engaged in progress of project.
- Interested in clinical care, but not required to be a clinician
- Willing to learn from, listen to, and work with staff to improve patient safety on the unit.
Slide 5: The Senior Executive’s Characteristics
(vignette still)
Click to play
Slide 6: Senior Executive’s Responsibilities

- Emphasizes effective communication.
- Meets monthly with the CUSP team.
- Supports the technical and adaptive work of change.
- Collaborates to develop and implement a plan addressing safety issues.
- Holds staff accountable for reducing patient harms.
Slide 7: The Senior Executive’s Roles and Responsibilities
(vignette still)
Click to play
Slide 8: Emphasizes Effective Communication

- Encourages transparent communication.
- Establishes clear goals for unit safety.
- Outlines clear project goals and expectations for leaders and staff on CUSP teams.
Slide 9: Meets Monthly With the CUSP Team
- Joins frontline staff and middle manager for rounds and a 1-hour monthly meeting.
- Considers patient risks and involves frontline personnel in creating ways to mitigate those risks.
- Reviews unit data with team and works with direct care providers to establish an improvement plan.
Slide 10: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change
Technical Work
- Addresses problems for which:
- the definition is clear.
- potential solutions are reasonably clear.
- solutions require minimal learning.
- Leaders and followers recognize their responsibility for implementing a solution.
- Teams have the resources necessary to succeed.
Slide 11: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change
Adaptive Work
- Addresses problems that require a change in:
- Attitudes.
- Beliefs.
- Behaviors.
- Leaders, staff, and key stakeholders share responsibility for change.
Slide 12: Supports Both Technical and Adaptive Work of Change

Technical Work
- Synchronizes with team members to create project goals and timelines and outlines the project mission.
- Coordinates with team members to ensure that necessary structures are in place - staff, roles, authority, and responsibility.
- Collaborates with team members to maintain the material needs of the project - budgets, resources, space, and staffing.
Adaptive Work
- Works with team members to clarify the decisionmaking, conflict management, and problemsolving processes.
- Coordinates with team members to verify that necessary evaluation mechanisms are in place.
Slide 13: Collaborates To Develop and Implement a Plan Addressing Safety Issues

- Considers patient risks identified in the Staff Safety Assessment with team members.
- Involves frontline providers to help reduce risks.
- Helps prioritize hazards and construct an improvement plan.
Slide 14: The Senior Executive’s Role on the Team
(vignette still)
Click to play
Slide 15: Holds Staff Accountable for Reducing Patient Harm

- Expects resistance and is prepared to address it
- Holds all team members, including executives, accountable for implementing the plan
Slide 16: The Challenges of Partnering With a Senior Executive

- Lack of clinical background.
- Lack of recognition for the value of CUSP.
- Unavailability to meet with the CUSP team regularly.
Slide 17: How to Engage Your Senior Executive and Develop Shared Accountability for the Work

- Acknowledge the senior executive’s perspective ("What’s in it for me?").
- Increase the visibility of your senior executive.
- Ensure an executive is assigned to each CUSP team and participates regularly in meetings.
- List identified safety issues in the Safety Issues Worksheet for Senior Executive Partnership or a tracking log.
Slide 18: Exercise

Questions to consider:
- What are some effective ways for leaders to work with staff to bring about a change?
- How can you use those methods to address the safety issues you identified in your organization?
- Using the Shadowing Another Professional Tool, what are some new insights about your colleagues’ work?
Slide 19: Engage the Senior Executive: What the Team Needs to Do

- The CUSP team leader or members of the safety team should meet with the senior executive before the executive holds safety rounds to share unit-specific information
- In preparation, gather relevant information about the unit for the senior executive.
- During executive safety rounds, the patient safety team, senior executive, and unit providers should review any safety issues identified and list them on a tracking log.
- In preparation for executive safety rounds, the unit champion should:
- Brief providers on the purpose of partnering with a senior executive.
- Ask them to be prepared to discuss their own safety concerns and suggestions for resolution during rounds.
Slide 20: Summary

- The senior executive does not need a clinical background, but should be an active team member.
- The senior executive is responsible for supporting effective communication, meeting with the CUSP team, understanding technical and adaptive work, collaborating with the team to address safety issues, and holding staff accountable.
- The 4 E’s and CUSP tools are great resources to help recruit a senior executive.
Slide 21: CUSP Tools

- Safety Issues Worksheet for Senior Executive Partnership.
- Staff Safety Assessment.
- CEO/Senior Leader Checklist.
- Infection Preventionist Checklist.
- Board Checklist.
- Shadowing Another Professional Tool.
Slide 22: References