CUSP Toolkit, The Role of the Nurse Manager, Facilitator Notes
Contents
Slide 1. Cover Slide.
Slide 2. Learning Objectives
Slide 3. What is a Nurse Manager?
Slide 4. Why Are Nurse Managers So Important?1, 2, 3, 4
Slide 5. The Nurse Manager's Dual Roles
Slide 6. Oversee Unit-Based Operations
Slide 7. The Leadership and Management Roles of the Nurse Manager
Slide 8. The Nurse Manager as a Mentor and Coach
Slide 9. Responsibilities of the Nurse Manager
Slide 10. Human Resource Management4
Slide 11. Encourage Professional Development of Staff
Slide 12. Customer Focus
Slide 13. Financial Responsibility
Slide 14. Standards of Care
Slide 15. Alignment with Organizational Goals5
Slide 16. Frameworks that are Useful for Nurse Managers
Slide 17. The Baldridge Health Care Criteria for Performance Excellence Framework6
Slide 18. Quint Studer's Five Pillars7
Slide 19. Balanced Scorecard8
Slide 20. The American Organization of Nurse Executives Nurse Manager Leadership Partnership Learning Domain Framework9
Slide 21. Measurement Tactics: Customer/Patient Focus
Slide 22. Work Alignment
Slide 23. Quality/Safety
Slide 24. Financial
Slide 25. Summary
Slide 26. CUSP Tools
Slide 27. TeamSTEPPS® Tools
Slide 28. References
Slide 29. References
Slide 30. References
Slide 1. Cover Slide

Say:
The Role of the Nurse Manager module of the Comprehensive Unit-based Safety Program (or CUSP) Toolkit addresses the role of nursing leaders for your quality improvement initiative. This module explains the responsibilities of the nurse manager, leadership and management roles of the nurse manager, key business and health care quality improvement frameworks, and quality measurement.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 2. Learning Objectives
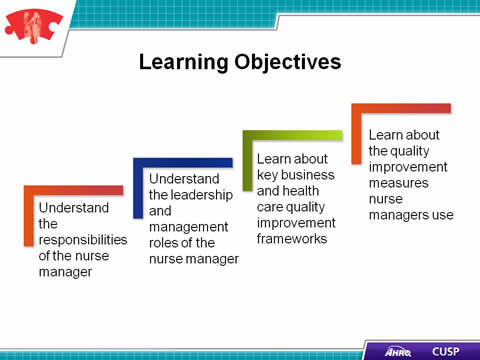
Say:
In this module we will:
- Detail the responsibilities of the nurse manager.
- Explain the leadership and management responsibilities of the nurse manager.
- Describe the key business and health care quality improvement frameworks.
- List the quality improvement measures nurse managers use.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 3. What is a Nurse Manager?

Say:
Nurse managers work with their staff to coordinate all aspects of daily patient care on the unit. By ensuring that staff, patients, and patients' families are communicating, nurse managers help unit staff members deliver the safest possible care.
Nurse managers:
- Embody both the nurse and executive roles.
- Typically report to a supervising nursing leader.
- Are responsible for the function of their unit.
The CUSP framework is a proven tool that nurse managers can use to improve the safety culture on their unit. Nurse managers are the leader of their unit and can influence the unit's culture and ability to embrace change. Nurse managers can support their unit's CUSP activities by integrating CUSP principles and tools into the unit's workflow. Because nurse managers are in a position to align the unit's goals and processes with a culture change framework, they play an integral role in the support of a unit's CUSP work.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 4. Why Are Nurse Managers So Important?1, 2, 3, 4

Say:
Nurse managers see the big picture on the unit and work to ensure the unit's workflows and its activities are aligned with the hospital's strategic plans.
Serving in this capacity, nurse managers are change agents on their unit. They work with staff to initiate new policies and procedures that help the unit team achieve their quality improvement goals and sustain their CUSP efforts. Nurse managers lead their unit staff in preventing patient harm in their unit, empowering nurses to be the first line of defense against patient harm.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 5. The Nurse Manager's Dual Roles

Say:
Nurse managers maintain two roles within the unit: They deliver clinical care and serve as administrative leaders on their unit. When nurse managers interact with an administrator, they wear one hat. When nurse managers interact with unit staff, they wear a different hat. These two groups can have different agendas, and the nurse manager has the unique position of understanding both groups. Nurse managers are a conduit for communication and comprehension between the two groups to move the unit toward the hospital's strategic goal.
Nurse managers can also apply their position to support the unit's CUSP work by engaging unit staff and hospital leaders. Nurse managers can help the CUSP team implement Just Culture principles on their unit to reinforce peer-to-peer coaching and mentoring. As part of their administrative duties, nurse managers can ensure the unit has the resources it needs to initiate and sustain its CUSP intervention.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 6. Oversee Unit-Based Operations
Do:
Play the video.
Ask:
How does the nurse manager on your unit maintain unit-based operations?
Identify areas within your CUSP team's work where your unit's nurse manager can assist your team. Try to identify one administrative and one staff-focused area for which your team would like help from unit-level management.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 7. The Leadership and Management Roles of the Nurse Manager

Say:
Nurse managers lead their unit staff by providing their vision for the unit's progress toward excellence. Nurse managers are the change agents for the unit and make decisions that guide the unit's activities. They work closely within their unit to inspire, motivate, and engage administrators, unit staff, and customers. (Customers are discussed later in this module.)
Nurse managers must manage all unit functions that affect patient care and must embody the skill sets needed to be effective leaders and managers.
As leaders, nurse managers:
- Embody the vision, mission, and values of the unit and share these with staff.
- Motivate staff to strive for professional excellence.
In their leadership role, nurse managers use a socio-adaptive skill set that encourages the use of teaching, coaching, and Just Culture principles to engage unit staff and support unit-based initiatives by ensuring close working relationships among unit team members.
As managers, nurse managers deal are responsible for:
- Unit operations.
- Finances and budgets for the unit.
- Strategic goal achievement.
Nurse managers in their management roles use a task-oriented, technical skill set. This skill set enables nurse managers to support the unit's work through working with the team to ensure the team has the necessary resources and materials needed to initiate and sustain their intervention.
Embodying these leadership and management skill sets in their daily work helps nurse managers successfully lead and manage the activities that take place on their unit while supporting the quality improvement work of their staff.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 8. The Nurse Manager as a Mentor and Coach
Do:
Play the video.
Ask:
Can you identify the traits of a good mentor and coach that were identified in the video?
Can you identify a nurse manager or nursing leader who you feel would be an excellent coach?
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 9. Responsibilities of the Nurse Manager

Say:
Nurse managers are responsible for managing human and financial resources; ensuring patient and staff satisfaction; maintaining a safe environment for staff, patients, and visitors; ensuring standards and quality of care are maintained; and aligning the unit's goals with the hospital's strategic goals.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 10. Human Resource Management4

Say:
Nurse managers are responsible for hiring, training, and developing employees; thus, nurse managers require strong coaching skills. When working with staff to achieve their human resources goals, nurse managers must obtain staff satisfaction feedback regularly. Once they analyze the feedback, they can develop a plan to start the programs and training staff members suggest. Nurse managers' work in this area supports the work of the CUSP team by providing a means of spreading training or methodologies using unit-wide curriculum.
When hiring staff, nurse managers ensure the unit's staffing needs are met in the most economical way possible so funds that would otherwise be used for recruitment can instead be spent on retaining high-performing staff.
In addition to hiring and training efforts, nurse managers work closely with staff on professional development. As staff members grow within their roles on the unit, nurse managers mentor staff members. These professional development opportunities allow nurse managers to hire from within when positions become open on the unit. Promoting positions internally and developing staff for these positions helps increase teamwork on the unit.
Nurse managers work with the staff to improve the systems on the unit by applying good system design. When nurse managers work with staff to develop good systems, they are supporting CUSP quality improvement efforts on their unit. By critically reviewing system-level breakdowns, nurse managers are working closely with unit staff to use the Science of Safety principles of safe design.
Nurse managers also manage behavior. Managing behavior calls for nurse managers to use empathy, coaching skills, and discipline when working with their staff. The Just Culture framework supports nurse managers' work because it engages staff and supports teamwork and communication on the unit. Further, it engages staff to collaborate and coach one another to deliver optimal levels of care.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 11. Encourage Professional Development of Staff
Do:
Play the video.
Ask:
Can you identify professional development opportunities on your unit? How will you work with the nurse manager on your unit to promote these opportunities?
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 12. Customer Focus

Say:
Nurse managers ensure the care delivered on their unit is customer focused. The hospital unit has numerous customers, and each has its unique needs and care delivery requirements. Nurse managers are responsible for ensuring the needs of customers are met.
Patient- and family-centered care
Nurse managers work with patients, families, and unit staff to develop patient- and family-focused care plans. Involving patients and their families in their care ensures the best possible care for the patient and creates a supportive and caring environment in which staff members are able to work closely with patients and their families.
Regulators
Nurse managers must also adhere to the requirements of regulatory agencies and organizations, such as the Joint Commission and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. The regulations of these organizations will determine almost all components of care delivery and staffing needs on the unit.
Local governments
Local governments take an active interest in the quality of care their local hospital delivers to the community. Nurse managers ensure the goals of the local government are embodied on the unit and community members receive the highest quality of care possible.
By engaging these customers, nurse managers ensure the unit is able to deliver the highest quality of care for their patients while adhering to regulations.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 13. Financial Responsibility

Say:
Nurse managers must understand of the following skills:
Budgeting
Nurse managers ensure the unit's expenses fall within its budget. This includes sharing financial expectations with unit staff so staff members are aware of the unit's financial goals.
Staffing costs
Nurse managers ensure staffing costs remain within the budgeted amounts. They prepare for fluctuations in staffing needs without accruing staff overtime, and when staffing needs overwhelm unit resources, they are responsible for budgeting for temporary help. Nurse managers also support the efforts of the CUSP team by helping the team develop a way for its work to be completed within available staffing resources.
Operating costs and physical plant costs
Nurse managers are responsible for the maintenance of operating and physical plant costs for the unit. They are responsible for ensuring these costs are kept at a minimum while making sure the needs of the unit are met.
Necessary equipment and supplies
The nurse manager makes sure that staff members have access to the equipment and supplies they need to complete their CUSP interventions. While the senior executive member of the CUSP team helps the team secure resources, it is the responsibility of the nurse manager to ensure that the team is able to effectively use those resources. When these items become expensive, the nurse manager needs to create a solution that satisfies the needs of their staff and does not compromised patient care.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 14. Standards of Care

Say:
Nurse managers understand the professional and regulatory guidelines (e.g., Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Joint Commission, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services) that govern patient care. Regulating agencies and insurance companies mandate that hospitals provide evidence-based clinical practices as the standard of care. Nurse managers are responsible for making sure their staff members are educated on standards of care and any changes to those standards so that staff members are able to provide the safest care possible on the unit.
Nurse managers assess compliance with standards and coach staff members who are not meeting the standards. Nurse managers work with their physician colleagues to determine the most up-to-date standards of care and to plan for them to be provided to their patients.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 15. Alignment with Organizational Goals5

Say:
Nurse managers are responsible for aligning the unit's goals with the hospital's goals. Nurse managers serve as the decisionmakers who are responsible for the best interests of the unit. They make sure unit staff members are able to clearly see how unit goals align with the hospital's goals.
Nurse managers encourage their staff to participate in projects and initiatives. Using the 4E's, nurse managers engage unit staff to participate in the project, educate them on the importance of their involvement, execute a plan of action with their staff, and evaluate their progress with the intervention being carried out on the unit.
When working with staff, nurse managers use more than one form of communication to share and receive information. By supporting effective communication on the unit, nurse managers are able to ensure their staff members have the necessary information to complete quality improvement work.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 16. Frameworks that are Useful for Nurse Managers

Say:
Hospitals, as businesses, employ frameworks to increase efficiency and quality of care. Some frameworks commonly seen in or adapted for health care include The Malcolm Baldridge Health Care Criteria for Performance Excellence, Quint Studer's Five Pillars, Balanced Scorecard, and the American Organization of Nurse Executives Nurse Manager Leadership Partnership Learning Domain Framework. These frameworks are proven in both the nursing and business worlds and deliver a results-driven protocol for nurse managers to follow when putting into effect business and health care quality improvement initiatives on their units. Nurse managers can support their unit's CUSP work through using other quality improvement frameworks. Using additional frameworks provides nurse managers with an additional reference point to gauge the success of the CUSP intervention and align the unit's work with it.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 17. The Baldridge Health Care Criteria for Performance Excellence Framework6

Say:
The Baldridge Health Care Criteria for Performance Excellence address the key areas of running a successful health care organization. These are:
- Leadership.
- Strategic planning.
- Customer focus.
- Measurement, analysis, and knowledge management.
- Workforce focus.
- Operations focus.
- Results.
The framework provides an integrated approach to performance excellence that nurse managers can use on their unit to make sure the unit is functioning at optimum efficiency and is engaging the appropriate stakeholders.
Nurse managers can use this framework to engage their unit staff with the intervention being implemented on the unit and ensure staff members are aware of the full systematic effects of their quality improvement work.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 18. Quint Studer's Five Pillars7

Say:
Quint Studer's Five Pillars provide a foundation for setting organizational goals, a direction for service, and an operational focus for nurse managers. When nurse managers align the strategy of the unit across the five pillars, the pillars provide the consistency and focus needed to sustain efforts over time.
The five pillars are:
- Service.
- Quality.
- People.
- Finance.
- Growth.
When nurse managers apply the Five Pillars to their unit's CUSP work, they are providing unit staff with another means of identifying their work with the unit's goals.
The service pillar is related to the quality of service that the unit staff delivers to patients and their families. When projects are aligned with this pillar, staff members are able to see where their work coincides with the service delivered to patients and their families.
The quality pillar is related to the quality improvement work that the unit staff members participate in as a part of their CUSP work. When unit goals are aligned with this pillar, the unit is able to see where their CUSP quality improvement work aligns with the goals of the unit.
Aligning goals with the people pillar provides nurse managers with a means of assessing how the CUSP intervention affects staff.
Aligning unit goals with the finance pillar provides nurse managers with a means of understanding how the CUSP intervention affects finances for the unit.
When unit staff and nurse managers align their goals with the growth pillar, they are evaluating their goals against measurable growth and development opportunities.
Evaluation is important for determining whether or not an intervention has been successful. The Five Pillars provide an evaluation process for an organization. When goals are strategically aligned across the five areas, deficiencies in one area are countered by excesses in another. Additionally, aligning goals across the Five Pillars helps keep the organization balanced in its short- and long-term objectives and encourages staff to develop goals that align with the pillars.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 19. Balanced Scorecard8

Say:
Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and measurement system that aligns business activities with the organization's vision and strategy, improves internal and external communications, and monitors organization performance against strategic goals.
The Balanced Scorecard measures:
- Customer results.
- Internal processes.
- Staff and organizational growth.
- Financial results.
- Vision and strategy.
Nurse managers can use the Balanced Scorecard when they want to measure the unit's progress. The scorecard is used as a strategic planning and measurement system for assessing all aspects of the unit. Nurse managers can apply this framework on the unit to obtain a greater understanding of the needs of the unit team.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 20. The American Organization of Nurse Executives Nurse Manager Leadership Partnership Learning Domain Framework9

Say:
The American Organization of Nurse Executives Nurse Manager Leadership Partnership Learning Domain Framework provides a means for aligning organizational goals and measuring progress toward goal achievement. The framework asks nurse managers to assess their business, personal development, and leadership functions on their unit when they develop goals and assess progress on the unit.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 21. Measurement Tactics: Customer/Patient Focus

Say:
Customer or patient satisfaction feedback, obtained using surveys, is another key tool that allows nurse managers to gauge the service the unit provides. These data, when analyzed frequently, provide nurse managers feedback that comes directly from patients and their families. This feedback helps nurse managers gauge the unit's performance and engagement with patients and their families. Once the feedback is reviewed, nurse managers share the information obtained from the surveys with the unit and hospital staff to ensure policies and procedures are aligned with the needs and interests of patients and their families.
These surveys provide a standardized approach for reviewing patient feedback and permits benchmarking across different departments and units within the hospital. Using these surveys, nurse managers can influence the quality of care that their staff members deliver to patients and their families.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 22. Work Alignment
Do:
Play the video.
Ask:
Can you identify ways in which your unit's work can be aligned with the quality improvement frameworks outlined in this module?
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 23. Quality/Safety

Say:
Nurse managers should obtain data on quality outcomes and adverse events monthly. Once these data are received, the nurse manager reviews the data to identify trends.
Nurse managers use quality and safety measurements to assess the care received on their unit. When working on an evidence-based initiative, teams can set improvement goals once they obtain baseline data.
Nurse managers use CUSP tools such as the Learning From Defects Tool to obtain staff feedback. The quality data from this tool will provide nurse managers with the information they need to work with staff to address the issues the tool raises. When working through the Learning From Defects process with staff, nurse managers involve the staff in the defect analysis process and in developing the action plan to address the issues the tool identified.
Additional quality and safety measurement tools include unit dashboards, newsletters, and staff meetings. These tools provide nurse managers and staff with opportunities to share ideas, create goals, and discuss progress with meeting or exceeding quality and safety goals. During staff meetings and dashboard discussions, staff members can collaborate to identify and solve barriers that are highlighted on the dashboard.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 24. Financial

Say:
Nurse managers collect financial data to deliver cost-effective care on the unit. Unless nurse managers can express the financial advantages of a change in process, the organization may not approve purchases of more hand hygiene dispensers, bar coding equipment, and other patient safety supplies. Quality and patient safety tasks may require more staff members to collect and analyze data and educate other staff. The professional staffing model uses the professional characteristics of the registered nurse and supports and sets expectations for their involvement in the quality and patient safety work done on their unit by building paid hours for quality improvement work into their schedule. During these hours away from patients, nurses attend quality meetings, complete research projects, and serve on hospital-wide quality and safety committees. This model has financial benefits for the unit because it schedules time for the nurses to work closely on cost-saving, quality improvement projects that will yield better outcomes for the entire unit.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 25. Summary

Say:
In summary, nurse managers support the quality and safety work of the unit by:
- Having an integral role in unit-based activities at their hospital.
- Serving as leaders and managers to their unit staff.
- Supporting their unit's CUSP work with other quality improvement frameworks.
- Measuring the success of their CUSP intervention by using additional quality improvement measures.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 26. CUSP Tools

Say:
In addition to the information presented in this module, CUSP tools are available online by visiting the AHRQ Web site: http://www.ahrq.gov/cusptoolkit.
These tools clarify the team members' roles and responsibilities and help assess unit team culture. They include the:
- Background Quality Improvement Team Information Form.
- Culture Check-up Tool.
- Daily Goals Checklist.
- Learn From Defects Form.
- Shadowing Another Professional Tool.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 27. TeamSTEPPS® Tools

Say:
Several TeamSTEPPS® tools also complement the material in this module by helping to improve team communication. The tools are available online at http://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/education/curriculum-tools/teamstepps/index.html.
[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 28. References

[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 29. References

[D] Select for Text Description.
Slide 30. References

[D] Select for Text Description.



