CUSP Toolkit: Spread Presentation Slides
Contents
Slide 1. Cover Slide
Slide 2. Learning Objectives
Slide 3. Definition of Spread1
Slide 4. Why Spread?
Slide 5. Spread Framework2
Slide 6. External Factors Affecting Spread3
Slide 7. Internal Factors Affecting Spread3
Slide 8. Factors That Affect Spread
Slide 9. What Facilitates Spread Success?4
Slide 10. Spread Sequencing5
Slide 11. Developing a Plan for Spread
Slide 12. Work With the Next Unit
Slide 13. Account for Variability
Slide 14. Exercise: Develop a Spread Plan To Decrease CAUTI Rates
Slide 15. Evaluate Spread
Slide 16. Seven Spreadly Sins5
Slide 17. Summary
Slide 18. Tools
Slide 19. References
Slide 20. References
Slide 21. References
Note: Slide content is presented below each of the images.
Slide 1. Cover Slide

(CUSP Toolkit logo)
Slide 2. Learning Objectives
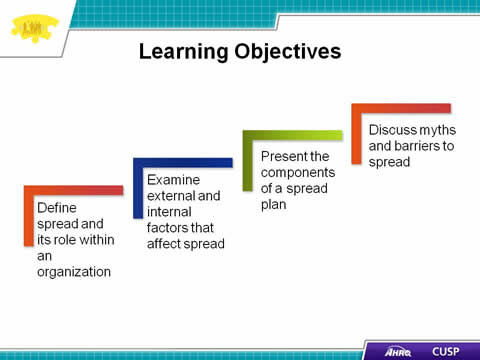
- Define spread and its role within an organization
- Examine external and internal factors that affect spread
- Present the components of a spread plan.
- Discuss myths and barriers to spread
Slide 3. Definition of Spread1

- "Spreading takes the process from the narrow, segmented population(s) or group(s) and broadens it to include all the population(s) or group(s) that will use the process."
- "Formalizing a process provides a reference to others; those new to the organization and those in the organization needing clarity about the specifics of the process."
Slide 4. Why Spread?

- Health care culture is local.
- Quality interventions target a process in small pilot projects usually on a local level (Lean Six Sigma, Plan-Do-Study-Act [PDSA]).
- Safety interventions targeted at the unit level (CUSP).
- Shifting the paradigm—from hierarchical to team culture.
Slide 5. Spread Framework2
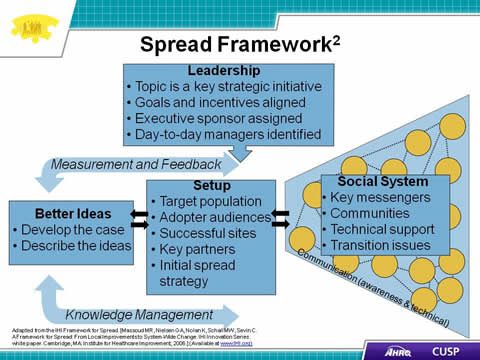
Leadership
- Topic is a key strategic initiative
- Goals and incentives aligned
- Executive sponsor assigned
- Day-to-day managers identified
Measurement and Feedback
Better Ideas
- Develop the case
- Describe the ideas
Setup
- Target population
- Adopter audiences
- Successful sites
- Key partners
- Initial spread strategy
Social System
- Key messengers
- Communities
- Technical support
- Transition issues
Communication (awareness & technical)
Knowledge Management
Adapted from the IHI Framework for Spread. [Massoud MR, Nielsen GA, Nolan K, Schall MW, Sevin C. A Framework for Spread: From Local Improvements to System-Wide Change. IHI Innovation Series white paper. Cambridge, MA: Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2006.] (Available at www.IHI.org)
Slide 6. External Factors Affecting Spread3

- Financial.
- Legal.
- Regulatory.
- Public opinion.
- Moral.
- Organizational priorities.
Slide 7. Internal Factors Affecting Spread3

- Leadership.
- Availability of resources.
- Knowledge and skill set.
- Organizational culture.
- Ongoing improvement efforts.
- Other priorities.
Slide 8. Factors That Affect Spread
Video vignette
Click to play.
Slide 9. What Facilitates Spread Success?4

- Evidence-based efforts, tools, and examples.
- Leadership support.
- Easy to adopt.
- Pertinent and relevant issue.
- Able to be piloted or tested on a small scale.
- Observable.
Slide 10. Spread Sequencing5
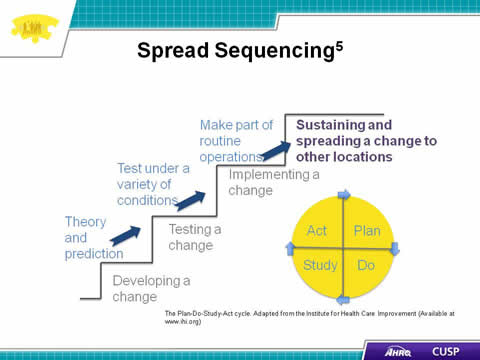
- Developing a change
- Theory and prediction
- Testing a change
- Test under a variety of conditions
- Implementing a change
- Make part of routine operations
- Sustaining and spreading a change to other locations
- Plan
- Do
- Study
- Act
The Plan-Do-Study-Act cycle. Adapted from the Institute for Health Care Improvement (Available at www.ihi.org)
Slide 11. Developing a Plan for Spread

- Inform the team.
- Work with the next unit to spread.
- Account for variability.
- Start with the units that can adopt easily.
Slide 12. Work With the Next Unit
Video vignette.
Click to play.
Slide 13. Account for Variability
Video vignette.
Click to play.
Slide 14. Exercise: Develop a Spread Plan To Decrease CAUTI Rates

- Goal: Decrease CAUTI rates on all floors.
- Care process: Use HICPAC Guidelines for catheter insertion and removal.
- Time: 3 months.
- Criteria to consider: Similar patient populations; similar physicians; staff receptiveness; unit leadership.
www.cdc.gov/hicpac/projects_in_progress.html.
Slide 15. Evaluate Spread

- Quantitative and qualitative approaches are essential for evaluating spread.
Slide 16. Seven Spreadly Sins5

- Start with large projects.
- Find one person willing to do it all.
- Expect vigilance and hard work to solve a problem.
- If a pilot project works then spread it unchanged.
- Require the person and team who drove the pilot project to be responsible for system-wide spread.
- Look at process and outcome measures quarterly.
- Expect marked improvement in outcomes early on without attention to process reliability.
Slide 17. Summary

- Spread helps organizations build on processes that originated at the local level.
- Organizations need to be prepared to address external and internal factors that can affect spread.
- An effective spread plan involves:
- Strong communication among the team
- Collaboration with other units
- Accounting for variability
- Identification of units able to adopt the process easily.
- Spread plan evaluation is ongoing.
Slide 18. Tools

Slide 19. References

- North Carolina Center for Hospital Quality and Patient Safety. North Carolina Prevent Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections Collaborative. North Carolina; 2010.
- Massoud MR, Donohue KL, McCannon CJ. Options for Large-Scale Spread of Simple, High-Impact Interventions (Prepared by University Research CO., LLC under Contract No. GHN-01-01-07-00003-00andGHN-0I-03-07-00003-00). Bethesda, MD: USAID Health Care Improvement Project; September 2010. www.hciproject.org/node/1650. Accessed April 15, 2012.
- Edson, B. Navigating the Fleet: Accelerating National Adoption. The Patient Safety Education Program (PSEP) Canada; February 2012.
Slide 20. References

- Cooley L, Kohl R. Scaling Up—From Vision to Large-Scale Change: A Management Framework for Practitioners. Washington, DC: Management Systems International; 2006. www.msiworldwide.com/files/scalingup-framework.pdf. Accessed April 15, 2012.
- Lloyd R. Applying the Science of Improvement to Daily Work. Chicago: HRET; 2012.
- Hagg HW, Workman-German J, Flanagan M, et al. Implementation of systems redesign: Approaches to spread and sustain adoption. In: Henriksen K, Battles JB, Keyes MA, et al., eds. Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches. Vol 2: Culture and Redesign. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2008. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK43727. Accessed April 14, 2012.
Slide 21. References

- Institute for Healthcare Improvement. Knowledge Center. How to Improve. www.ihi.org/knowledge/Pages/HowtoImprove/default.aspx. Accessed April 10, 2012.
- Massoud MR, Nielsen GA, Nolan K, et al. Framework for Spread: From Local Improvements to System-Wide Change. Cambridge, MA: Institute for Healthcare Improvement; 2006. IHI Innovation Series White Paper. www.IHI.org. Accessed April 10, 2012.