Module 6: Care for the Caregiver
AHRQ Communication and Optimal Resolution Toolkit
Facilitator Notes
|
Say: Module 6 includes information on the Care for the Caregiver component of the CANDOR process, which focuses on providing emotional support to caregivers following a CANDOR event. This module includes steps for establishing a Care for the Caregiver program at your organization. |
Slide 1
|
|
Say: Despite their effort to provide the best care possible to patients, health care providers are sometimes faced with the aftermath of adverse patient harm events. Caregiver grief following a CANDOR event can be devastating, especially as the initial response to a CANDOR event focuses on the needs of the patient and/or family. Organizations can demonstrate support for the caregivers by developing and implementing a Care for the Caregiver program—sometimes referred to as a program that addresses the needs of the "second-victim."At the end of this module, the participant will be able to:
|
Slide 2
|
|
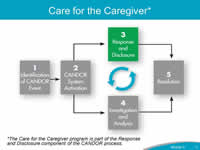
Say: The Care for the Caregiver program should be initiated as part of the Response and Disclosure component of the CANDOR process. Module 5 provides detailed information concerning the elements of disclosure to patients and families following a patient harm event. It is also important to provide care and support to the caregivers following a CANDOR event. |
Slide 3
|
|
Say: The organization should first establish a team or task force that will be responsible for developing, implementing, and maintaining the Care for the Caregiver program for the organization. This team will also help identify and develop supporters, including peer supporters, who will provide the caregiver services. The following are suggestions for the Care for the Caregiver team composition, as well as peer supporters, who will assure this component of the CANDOR process is fully developed.
The Care for the Caregiver program should include a "fast track" process that allows the caregiver to quickly access support and guidance following a patient harm event. |
Slide 4
|
|
Say: Once the team leaders and members are identified, the team will need to define the Care for the Caregiver team infrastructure for their organization, which includes the process of how support will be provided to caregivers. The team should seek administrative support prior to developing the program to confirm that the team will initially activate the Care for Caregiver program only following a CANDOR event. As the program becomes more established and clinicians feel comfortable with the new process, the team may expand the scope of services and activate the program for other patient events or errors. The key steps for developing the Care for the Caregiver team infrastructure include:
|
Slide 5
|
|
Say: Multiple studies have shown that involvement in medical errors and adverse events can take a significant toll on clinicians. It is estimated that one in seven patients is affected by adverse events, and that as many as half of all clinicians will be involved in a serious adverse event at least once during their career.The patient and the family are the first victim(s) after an event, but the second-victim is the caregiver(s) involved in the event. Frequently, these individuals may feel personally responsible for the patient outcome and that they have failed the patient, second-guessing their clinical skills and knowledge base. Dr. Wu discusses this concept in his article "Medical Error: The Second-Victim" and the associated "expectation of perfection". The CANDOR process embraces Just Culture principles, which recognize that "active" errors represent predictable interactions between human operators and the systems in which they work. A number of scenarios that are prone to the development of second-victims include, but are not limited to:
When a caregiver becomes a second-victim, the provision of support should extend beyond the individual caregiver and embrace the entire care team involved in the unanticipated patient harm event. |
Slide 6
|
|
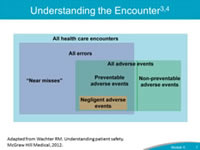
Say: As referenced in Module 3, this diagram shows the distinction between adverse events and errors, and recognizes that not all adverse events are medical errors, and not all medical errors are adverse events. This distinction is important, even though some degree of emotional distress is likely when a clinician is involved in any error or adverse event, regardless of severity.Providers can experience the negative effects of the second-victim phenomenon even in cases where no adverse event occurred, but they feared that an error may have occurred. Providers can also experience profound problems after adverse events that were not associated with medical error, such as an unexpected death after elective surgery in a healthy patient where nothing is found to have been done wrong even after careful review. Therefore, it is important to recognize the distinction between medical errors and adverse events, as providers can become second-victims with either. For the remainder of the module, we will use the term "event" when discussing activation of the Care for the Caregiver program in response to a CANDOR event. |
Slide 7
|
|
Say: Second-victims can have specific concerns and symptoms following a CANDOR event. For example, second-victims might worry about the patient, themselves, their peers, and the future. The second-victim is often concerned about whether or not the patient and family are okay after the event and about how the event might impact their career or job. Many second-victims worry about how their peers will view them after the event, whether or not their colleagues will trust them to deliver safe care to patients, and if the organization is going to react negatively to the event.A Care for the Caregiver program can be structured to help the second-victim through a peer support process designed to address any concerns or worries experienced by the second-victim. Additionally, the program can help caregivers deal with any physical or emotional symptoms experienced following the CANDOR event. These symptoms can include the ones listed on this slide. The CANDOR process acknowledges and promotes the need for a caregiver program to support all team members following an unexpected patient harm event. |
Slide 8
|
|
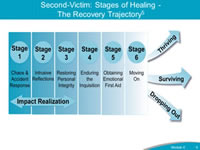
Say: The stages of healing after an unanticipated patient harm event are much like the stages of grief and have been described in the literature as the Recovery Trajectory.The Recovery Trajectory has six stages. Stages 1 through 3 may occur individually or simultaneously. Throughout all stages, individuals may experience physical and/or psychosocial symptoms. A second-victim may relive the "initial" event when a similar clinical situation is presented. The reliving of the event is also known as a "tripping" or "triggering" event and can occur when the second-victim is going through stages 2-6. On the next few slides, we will explore each stage and how a Care for the Caregiver program can support the second-victim at each stage. |
Slide 9
|
|
Say: The first stage of the Recovery Trajectory is the chaos and accident response. This stage is characterized by either the second-victim realizing that an event has occurred, or the organization recognizing that an event has occurred. During this stage, the second-victim might tell someone about the error/event as their way of asking for help. The second-victim might not be able to continue to care for the patient involved and might request reassignment. The second-victim might not be able provide care in the room where the event occurred and might appear distracted and/or experience a wave of emotions.An example of the emotions, feelings, and reactions a second-victim might experience are described in the following quote from an anonymous second-victim: "Right after the…code, I was having trouble concentrating. It was nice to have people take over… that I trusted. I was in so much shock, I don't think I was useful." The Care for the Caregiver program can assist the caregiver in this stage by identifying and contacting the second-victims after the event, and assessing the ability of staff member(s) to continue to work after the event. |
Slide 10
|
|
Say: The next stage is intrusive reflections. This stage is characterized by the second-victim re-evaluating and dwelling on their involvement in the event, and potentially isolating themselves from co-workers, family, and support systems. The event might produce feelings of internal inadequacy, either because the event occurred or because of the emotions the second victim is experiencing.An example of the emotions and thoughts that can occur at this stage from a second-victim are in the following quote from an anonymous second-victim: "I started to doubt myself… I thought maybe if I'd have done something another way, it wouldn't have happened… but everything was more clear, looking at things in retrospect. I lost my confidence for some time." The organization can assist the caregiver experiencing stage 2 by ensuring that the Care for the Caregiver program has been activated and caregiver team members are aware of those who need support. During this phase, it is important that organizational resources observe the second victim(s) for the presence of lingering physical and/or psychosocial symptoms. |
Slide 11
|
|
Say: Stage 3 focuses on restoring personal integrity. This stage is characterized by the second-victim gaining acceptance from coworkers by feelings that the gossip regarding the event has been managed or minimized. The second-victim is often fearful at this point about what is going to happen next and whether or not they will be able to regain the trust of their colleagues.An example of the thoughts and emotions during this stage from a second-victim are contained in the following quote from an anonymous second-victim: "Every single day for months, I'd walk in and think, 'Everyone knows what happened.' I thought, 'These people are never going to trust me again.'" The Care for the Caregiver program can assist the caregiver in this stage by assuring that management oversight of the event continues, completing the event report, supporting leadership as they manage the unit/team's overall response or "rumor control," and evaluating whether an event debrief is indicated for the entire team. |
Slide 12
|
|
Say: The next stage is called "Enduring the Inquisition." During this stage, the second-victim often realizes the seriousness of the event and has, or is in the process of, responding to many CANDOR Response Team members concerning the "whys" about the event. The second-victim understands that disclosure of the event will occur with the patient and/or family and might be concerned about whether the patient and/or family will choose to sue the organization.The thoughts and feelings a second-victim might experience during this stage are described in the following quote: "I didn't know what to do or who to talk to professionally or legally. Clearly, I know we needed to keep that quiet—it might have been helpful to be able to talk to someone else, but I couldn't do that." The Care for the Caregiver program can assist the caregiver enduring the inquisition by identifying key individuals involved in the event, developing an understanding of what happened, and supporting the individual(s) involved in event. |
Slide 13
|
|
Say: Stage 5 is characterized by the second-victim seeking personal or professional support from the organization or indicating an interest in getting help or support from outside of the organization. This stage can be seen in the following quote from one anonymous second-victim: "There was nobody I could tell, not even my husband. All I could say was, 'I've had a really horrible day.'"The Care for the Caregiver program can assist the caregiver experiencing stage 5 by ensuring the organization's emotional response plan is in progress and that, if needed, the patient safety/risk management representatives are available to support the caregiver(s). |
Slide 14
|
|
Say: The final stage of the recovery trajectory is Stage 6 "Moving On." Three possible results can come out of this stage of the trajectory:
|
Slide 15
|
|
Say: An important component of the Care for the Caregiver program includes identifying peer supporters. Peer supporters need to understand the different levels or tiers of support that can be offered to second victims. Tier 1 or Local Support: Involves support from the department leaders and colleagues/peers. This group can provide one-on-one reassurance to the second-victim. Tier 2 or Trained Peer Supporters: Individuals who provide one-on-one crisis intervention and peer support mentoring to the second-victim through the investigation and analysis phase, and potentially through litigation. Tier 3 or Expedited Referral Network: Additional referral resources to help support the second victim throughout the recovery trajectory. Additional details on each of these tiers are available in the Care for the Caregiver support program tools. |
Slide 16
|
|
Say: Tier 1 involves support from the department leaders and the second-victim's colleagues/peers. In this tier, department leaders should connect with the clinical staff involved in the event and reaffirm their confidence in the clinical staff involved in the event. The department or CANDOR Response Team should consider calling in flex staff to relieve the clinical staff involved in the event, notify clinical staff involved in the event what is going to happen next, and keep them informed throughout the post-event period. The most important aspect of this level of support is checking on the involved staff regularly.While the support of the department leader is important to the second-victim, so is the support from their colleagues/peers. The colleagues/peers of the second-victim can provide support by being "there" for the victim by practicing active listening skills when talking with the co-worker, and offering appropriate support without asking about specific details of the event. The focus during this tier is the feelings of the coworker and their emotional support. |
Slide 17
|
|
Say: Tier 2 support typically is provided by members of the Care for Caregiver program or initially by the CANDOR Response Team. All of these individuals should be trained to provide one-on-one support for the second-victim and to determine if the clinical team needs to conduct a team debriefing. If the team needs to debrief, the trained peer supporters can help facilitate the debrief. These individuals are also responsible for determining if it is safe for the caregiver involved in the event to continue with their duties, or if relief personnel need to be brought in to ensure patient care remains safe.This level of support is given not only at the time of the event, but also as needed by the second-victim during the recovery trajectory. |
Slide 18
|
|
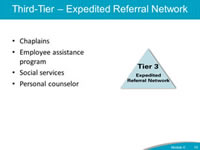
Say: Tier 3 support recognizes the needs of the second-victims and the trained peer supporter(s). If the trained peer supporter determines the needs of the second-victim are beyond the level of support they can provide, then the trained peer supporters should pursue additional resources to help the second-victim.The organization should develop relationships with additional resources such as chaplains, employee assistance program contacts, social services, and personal counselor(s) during the development of the Care for the Caregiver program. These resources can offer unique and valuable additional support during this tier. Tier 3 support acknowledges the limitations of an organization's trained peer supporters and reinforces the importance of pursuing additional help to meet the commitment to the caregivers and the organization's vision for a CANDOR process. |
Slide 19
|
|
Say: An organization may experience a number of challenges when providing peer support as part of the Care for the Caregiver program. Some of these challenges include:
An effective peer support system can help address all these challenges. |
Slide 20
|
|
Say: The two primary activities involved in peer support are talking through the experience and walking through the peer support interaction:
On the next few slides are videos that demonstrate how to conduct a peer support interaction. |
Slide 21
|
|
Say: The following videos will help you understand how a peer support interaction can occur with a physician and a nurse. |
Slide 22
|
|
Say: While the Care for the Caregiver program typically focuses on providing assistance to an individual following a patient harm event, the organization may also need to prepare to provide peer support for a team. An emotional group debriefing may be a beneficial peer support service if an entire team was impacted by a patient harm event. It is important that this type of session be led by a trained peer supporter. Additional peer supporters known as "lifeguards" should be present to observe during the debrief, to support those having difficulty during the group debriefing, or to ensure there are additional people available to conduct followup with individuals after the debrief. |
Slide 23
|
|
Slide 24
|