Contents
Appendix A.1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Algorithm for Identifying Inpatient Hospital Services Classified as Ambulatory Sensitive.
Appendix A.2. Definition of Project Service Categories based on IHS Clinic Codes.
Appendix A.3. Definition of Dedicated Education and Case Management Visits.
Appendix A.4. Health Status Measures: Condition Categories and Morbidity Burden.
Appendix A.5.Process Employed to Estimate Treatment Costs for Indian Health Service and Tribally Provided Health Services
Appendix A.1. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Algorithm for Identifying Inpatient Hospital Services Classified as Ambulatory Sensitivea
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) developed an array of health care decision making and research tools that may be used by public health agencies, health care systems, researchers, and others at the Federal, State and local levels. The Quality Indicators (QIs) are measures of health care quality that make use of readily available hospital inpatient administrative data. According to AHRQ, the QIs may be used to highlight potential quality concerns, identify areas that need further study and investigation, and track changes over time.
The Prevention Quality Indicators (PQIs) are a set of measures that may be used with hospital inpatient discharge data to assess the quality of care for "ambulatory care sensitive conditions." These are conditions for which outpatient care may potentially prevent the need for hospitalization or for which early intervention may prevent complications or more severe disease. With high-quality, community-based primary care, hospitalization for these illnesses may be avoided. For example, patients with diabetes may be hospitalized for diabetic complications if their conditions are not adequately monitored or if they do not receive the patient education needed for appropriate self-management. Although factors outside the direct control of the health care system influence inpatient service utilization, such as environmental conditions or lack of patient adherence to treatment recommendations, the PQIs provide a starting point for assessing quality of health services in a community.
Because the PQIs are calculated using readily available hospital administrative data (i.e., patient data found in a typical hospital discharge abstract), they are an easy-to-use and inexpensive “screening tool.” They may be used to help flag potential health care quality problem areas that need further investigation and to provide a quick check on primary care access or outpatient services in a community. They may be used to identify unmet community health care needs, monitor how well complications from a number of common conditions are being avoided in the outpatient setting, and compare performance of local health care systems across communities.
a This information was extracted from the AHRQ website: http://www.qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/modules/pqi_overview.aspx.
Other information, such as the technical specifications for specific measures, may be obtained at: http://www.qualityindicators.ahrq.gov/modules/pqi_resources.aspx.
Appendix A.2. Definition of Project Service Categories based on IHS Clinic Codes
Outpatient service utilization is reported by Service Category. Below are the IHS Clinic Codes included in each Service Category.
| Primary/General | Behavioral |
|---|---|
| General | Mental Health (Psychiatry) |
| Family Practice | Behavioral Health |
| Pediatric | Alcohol And Substance |
| Immunization | Medical Social Services |
| Gynecology | Day Treatment Prog |
| Internal Medicine | |
| Obstetrics | Cardiology |
| Nurse Clinic | Cardiology |
| Women's Health Screening | |
| Well Child | Endocrinology |
| EPSDT | Endocrinology |
| Chronic Disease | |
| General Preventive | Nephrology |
| Labor And Delivery | Nephrology |
| Family Planning | |
| Employee Health Un | Other Specialty |
| Wellness | Surgical |
| Pain Management | Orthopedic |
| Teen Clinic | ENT |
| High Risk | Day Surgery |
| Postpartum | Wound Care |
| Evening | Rheumatology |
| Elder Care | Urology |
| Perinatogist | Neurology |
| Cancer Screening | Cancer Chemotherapy |
| Hypertensive | Pulmonology |
| Men's Health Screening | Gastroenterology-Hepatology |
| Oncology-Hematology | |
| Diabetes Clinic | Neurosurgery |
| Diabetes Clinic | Plastic Surgery |
| Dental | Eye |
| Dental | Optometry |
| Ophthalmology | |
| Emergency | Diabetic Retinopathy |
| Emergency Medicine | Retinopathy |
| Observation | |
| Foot | |
| Urgent | Podiatry |
| Urgent Care | Diabetic Foot Clinic |
| Physical Therapy | Ancillary |
| Physical Therapy | Laboratory Services |
| Sports Medicine | Radiology |
| Audiology | |
| Other Therapy | Ultrasound |
| Occupational Therapy | Mammography |
| Speech Pathology | Computed Tomography |
| Rehabiliation | Respiratory Care |
|
|
Dialysis Laboratory Services |
| Home | Colposcopy |
| Home Care | Radiation Exposure Screening |
|
|
Teleradiology |
| Public Health | |
| PHN Clinic Visit | Ambulance |
| Ambulance | |
| Diabetes Clinic | |
| Diabetes Clinic | Other - non Office visits |
| Chart Rev/Rec Mod | |
| Other Office Visits | Telephone Call |
| Complementary Medicine | W. I. C. |
| Other | Follow-Up Letter |
| Dermatology | NIH Clinic |
| Traditional Medicine | Radio Call |
| Chest and TB | Telemedicinea |
| Ryan White Early Intervention | |
| Chiropractic | OTC Medications |
| Health Aide Clinic | PH Preparedness (Bioterrorism) |
| Devel. Assessment | Indirect |
| Crippled Children | Dialysis |
| STD | a For some sites we will include Telemedicine as a specific service (e.g., radiology, nephrology). |
| Pharmacy | |
| Pharmacy | Education/Case Management* |
| Diabetes Education-Individual | |
| School | Diabetes Education-Group |
| School | Diabetes Clinic - some providers* |
| Case Management Services | |
| Triage | Dietary |
| Triage | Education Classes |
| Grouped Services | |
| Tobacco Cessation Clinic | |
| Obesity | |
| Maternity Case Mgmt Supp Serv |
* Defined by provider, clinic, and procedure codes. Key clinic codes are listed above.See Appendix A.3.
Appendix A.3. Definition of Dedicated Education and Case Management Visits
Overview
One of the goals of the AHRQ/IHS Improving Health Care Delivery Data Project was to examine the use of education and case management services for persons with diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Each of the 14 project sites provides education and case management (ECM) services using different types of health professionals who work in a number of different clinics. In collaboration with the project’s Steering and Health Information Committees, AHRQ/IHS project staff developed an algorithm to identify the provision of such services.
The algorithm uses available information in the IHS National Data Warehouse (NDW) on provider type, clinic type, and procedure codes to identify visits conducted specifically for ECM, while recognizing that education and case management are also provided during general primary care and diabetes clinic visits, and by telephone.
Algorithm for Education and Case Management Visits
In this document, we outline the basic algorithm used to identify five types of ECM visits. This algorithm was adapted for use in each project site as deemed necessary. The five types of visits are:
- Diabetes education;b
- Nutrition education;
- Case management;
- Clinical pharmacy (i.e., visits conducted by clinical pharmacy specialists, or clinical pharmacists, who provide services using an advanced practice pharmacy model; and
- Other health education.
The algorithm allows for a person to have one visit per day (e.g., case management and diabetes education). If more than one type of health personnel provided services during an ECM visit, the record for one provider was chosen using a ranking based on provider type.
Education Algorithm
- Identify five different types of ECM visits and keep one record per person per day per type of visit for analysis using the following criteria:c
-
Diabetes Education includes visits identified by the following definition:
Clinic codes: Diabetes education - Group or Diabetes Education – Individual AND Provider types: 1-Clinic RN; 2- Pharmacist, Pharmacy Practitioner, or Clinical Pharmacy Specialist; 3-Health Educator; 4-Licensed Practical Nurse; 5-Public Health Nurse; or 6- Health Aide.
Nutrition Education includes visits identified by the following two definitions:
1- Provider types: Dietitian, Nutritionist, or Tribal/Contract Nutritionist AND Clinic codes: 1- Diabetes Education – Group, Diabetes Education – Individual; 2- Dietary; 3- Education Classes; 4- Obesity; 5- Grouped Services; 6- Tobacco Cessation Clinic; 7- Maternity Case Management Support Services.d
OR
2 – Clinic Code: Dietary AND Provider types: 1-Clinic RN; 2-Licensed Practical Nurse; 3-Public Health Nurse; or 4-Health Aide
For each visit, reported Medical Nutrition Therapy procedure codes were identified when possible.
-
Case Management includes visits identified by the following two definitions:
1 - Provider type: Case Manager
OR
2 - Clinic code: Case Management AND Provider types: 1-Clinic RN; 2-Pharmacist, Pharmacy Practitioner, or Clinical Pharmacy Specialist; 3- Licensed Practical Nurse; 4-Public Health Nurse; 5-Health Aide
-
Clinical Pharmacy includes visits identified by the following three definitions:
1 - Provider types: 1- Clinical Pharmacy Specialist; 2- Pharmacy Practitioner; 3- Pharmacist AND Procedure codes: one of the 3 Medical Therapy Management procedure codes
OR
2 – Clinic code: Diabetes Clinic AND Provider types: 1-Pharmacist; 2-Pharmacy Practitioner; 3- Clinical Pharmacy Specialist only if a project site indicated this was appropriate.
OR
3 – Clinic code: Anticoagulation Therapy or Medication Therapy Management AND Provider types: 1-Pharmacist; 2-Pharmacy Practitioner; 3- Clinical Pharmacy Specialist
-
Other Health Education includes visits identified by the following two definitions: Clinic codes: Obesity, Education classes, Grouped Services, Tobacco Cessation Clinic, or Maternity Case Management Support Services AND Provider types: 1-Clinic RN; 2-Pharmacist, Pharmacy Practitioner, or Clinical Pharmacy Specialist; 3- Licensed Practical Nurse; 4- Public Health Nurse; 5- Health Aide; 6- Community Health Representative.
OR
Provider type: Health Educator AND the visit was not otherwise identified.
-
- Ensure that only one visit record per person per day per type of education or case management is included in the ECM data. If more than one visit record for one type of education within one day exists, the visit record with the highest ranking provider is kept as specified in footnote 2.
b It is important to note that there is no provider code for Certified Diabetes Educator.
c The numbers (i.e., 1-, 2-, 3-) represent the rank given each provider type. If more than one record for each type of education exists for a clinic visit within the same day, the highest ranking visit is keep.
d Only specific types of Clinic codes were included in the list to avoid counting services that may not be education or case management (e.g., non-patient services)
Appendix A.4. Health Status Measures: Condition Categories and Morbidity Burden
I. Conditions
Verisk Risksmart software uses ICD-9-diagnosis codes to identify health conditions that clinicians diagnosed patients with. For this project, we used information on specific conditions to create the condition categories listed below. Table A.4.1 lists the specific types of conditions that are included in each health condition category.
- Hypertension
- Cardiovascular conditions:
- Ischemic heart disease
- Congestive heart failure and other forms heart disease
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Vascular disease
- Renal disease/failure
- Renal failure
- Neuropathy
- Amputations
- Transplant (e.g., liver, heart, bone marrow)
- Mental health disorders
- Depression
- Substance abuse disorders
- Tobacco use disorders
- Liver disease
- Eye disease
II. Medical service utilization records included as input into the software
Verisk recommends using only the diagnoses recorded by trained clinicians to identify the health conditions a person has. Table A.4.2 includes the list of services, defined by IHS clinic codes, for which IHS/Tribal service utilization records were included in data files as input into the software. Table A.4.3 provides a list of services that were excluded from the analysis. The list includes laboratory and imaging tests as the test may be conducted to rule out a diagnosis. It also excludes services (e.g., transportation) for which the records may not include accurate diagnosis codes.
Table A.4.2. IHS/Tribal medical service utilization records included as data input for the Verisk risk-adjustment software
| Primary | Cardiology | Emergency |
| General | Cardiology | Emergency Medicine |
| Family Practice | Endocrinology | Observation |
| Pediatric | Endocrinology | Urgent |
| Gynecology | Nephrology | Urgent Care |
| Internal Medicine | Nephrology | Dental |
| Obstetrics | Other Specialty | Dental |
| Women's Health Screening | Surgical | Third Party Dental |
| Well Child | Orthopedic | Eye |
| EPSDT | ENT | Optometry |
| Chronic Disease | Day Surgery | Ophthalmology |
| General Preventive | Wound Care | Diabetic Retinopathy |
| Labor And Delivery | Rheumatology | Retinopathy |
| Employee Health Un | Urology | Foot |
| Wellness | Neurology | Podiatry |
| Dermatology | Cancer Chemotherapy | Diabetic Foot Clinic |
| Pain Management | Pulmonology | Home |
| Teen Clinic | Gastroenterology-Hepatology | Home Care |
| High Risk | Oncology-Hematology | Public Health |
| Postpartum | Neurosurgery | PHN Clinic Visit |
| Evening | Plastic Surgery | Education/Case Management |
| Chest and TB | Surgical Outpatient Use Of Inp Trtmnt Room | Diabetic |
| Pediatric Outpatient Use Of Inp Trtmnt Rm | Diabetes Education-Individual | |
| Ryan White Early Intervention | Diabetes Education-Group | |
| Elder Care | Behavioral | |
| Perinatogist | Mental Health (Psychiatry) | |
| Cancer Screening | Behavioral Health | |
| Hypertensive | Alcohol And Substance | |
| Men's Health Screening | Medical Social Services | |
| Day Treatment Prog |
Table A.4.3. IHS/Tribal Service utilization records excluded from the Verisk software analysis.
| Ancillary | Other office visits | Other records (not visits) |
| Laboratory Services | Immunization | Chart Rev/Rec Mod |
| Radiology | Nurse Clinic | Telephone Call |
| Audiology | Complementary Medicine | W. I. C. |
| Ultrasound | Other | Follow-Up Letter |
| Mammography | Family Planning | NIH Clinic |
| Computed Tomography | Health Aide Clinic | Radio Call |
| Respiratory Care | Traditional Medicine | Telemedicine a |
| Dialysis Laboratory Services | Chiropractic | |
| Colposcopy | Devel. Assessment | OTC Medications |
| Radiation Exposure Screening | Default Code For Nulls/Blanks | PH Preparedness (Bioterrorism) |
| Teleradiology | Crippled Children | Indirect |
| Ambulance | Infant Stimulation | Dialysis |
| Ambulance | Fetal Alcohol Syndrome | a For some sites we will include Telemedicine as a specific service (e.g., radiology, nephrology). |
| Pharmacy | Other - non Office visits | |
| Pharmacy | Education/Case Management | |
| School | Case Management Services | |
| School | Dietary | |
| STD | Education Classes | |
| STD | Grouped Services | |
| Triage | Tobacco Cessation Clinic | |
| Triage | Obesity | |
| Maternity Case Mgmt Supp Serv | ||
| Genetics | ||
| Wisewoman |
Appendix A.5. Process Employed to Estimate Treatment Costs for Indian Health Service and Tribally Provided Health Services
- We estimated the costs of providing 13 types of health services.
- The 13 services include:
a hospital inpatient day, and 12 types of hospital outpatient services.
| Emergency room Urgent Eye care Dental Behavioral health Home visits |
Primary/General Specialty Foot care Education/Case management PT and other rehabilitative care Public Health Nurse clinic |
Primary Data Source
- Indian Health Service and Tribal Health Program (I/T) costs of providing services are recorded in the Centers for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) Cost Reports. The EighteenNineteen Group, Inc. compiles the Cost Reports for the Indian Health Service (IHS). The information is used to determine the IHS Medicaid and Medicare reimbursement rates.
- The Cost Reports include all costs of operating the I/T facilities. They costs are compiled into CMS cost categories called CMS Line Numbers.
- We collaborated with the EighteenNineteen Group to develop a process for using the Cost Report data, data on provided services, and information obtained from the project sites to estimate the costs of providing the 13 types of health services.
Service Cost Estimation Process
Figure A.5.1. Cost Estimation Process.
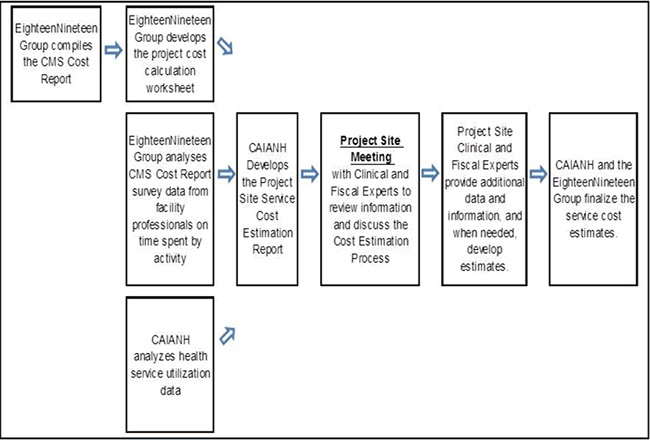
Since the NDW data do not include the costs of IHS service provision, IHS Cost Report data were used to estimate the costs of providing Indian Health Service (IHS) and Tribal (I/T) services. The IHS Cost Reports were prepared by a financial consulting firm, the Eighteen Nineteen Group, Inc., using a cost accounting process developed by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget to establish Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates for I/T-provided services. The Cost Report data extracts included data on all costs for providing services, such as those for all types of personnel, ancillary services, pharmacy services, supplies, capital and operating expenditures, and administrative services. Algorithms were developed to use the Cost Report data, NDW utilization data, project site fiscal information and utilization data not in the NDW, and expert opinion to estimate site-specific I/T service costs for 13 Cost Service Categories. All Service Categories map to one Cost Service Category. The average IHS cost for providing I/T services was estimated for each person in the project population based on his or her service utilization and the estimated average cost of providing those services in the project site.
Five strategies were used to allocate I/T facility costs to the different types of health services
- Allocate by CMS Line Number (50-60% of total costs)
- Allocate using utilization data (20-30% of total costs)
- Allocate using utilization data and information on services provision (10-12% of total costs)
- Allocate using utilization data, local data, and expert opinion (12-15% of total costs)
- Allocate using local data and expert opinion (<0.05% of total costs)
Figure A.5.2. Strategies used to allocate I/T facility costs.
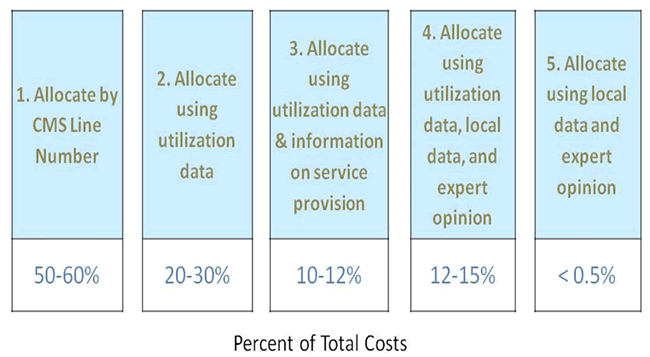
Figure A.5.3. Allocate by CMS Line Number
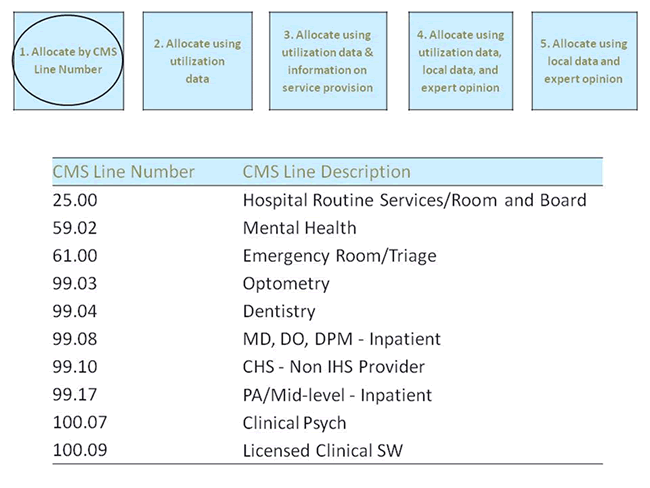
For some services, costs recorded by CMS Line Number were allocated to specific types of services (e.g., hospital routine services, mental health and dentistry).
Figure A.5.4. Allocate using utilization data.
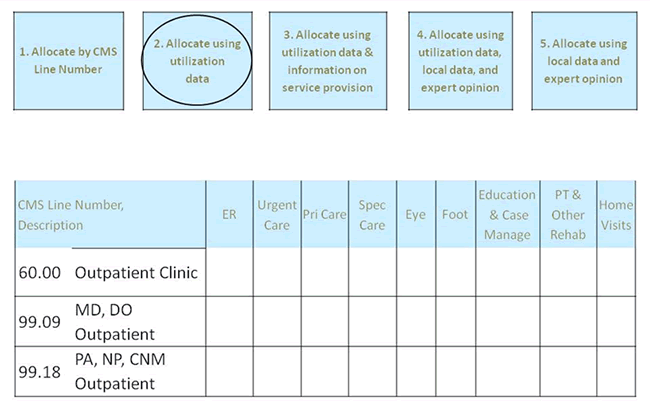
For some services, costs recorded by CMS Line Number were allocated to specific services based on utilization of those services. For example, physician outpatient costs were allocated to service categories based on utilization of those services.
Figure A.5.5. Allocate using utilization data and information on service provision.

Project site information on the provision of education and case management (ECM) services and home services to allocate costs associated with these services.
Figure A.5.6. Allocate using utilization data, local data, and expert opinion.
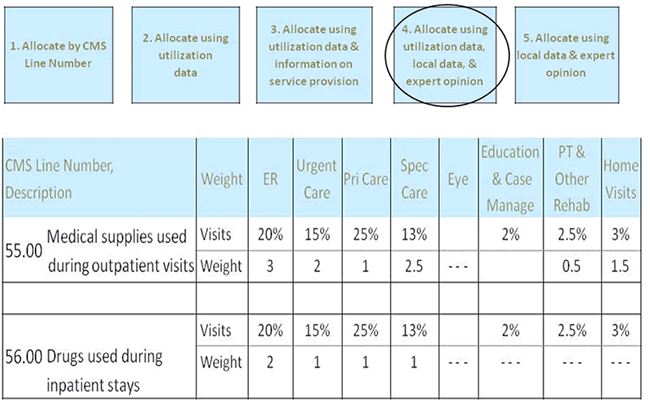
Medical service utilization data, data provided by the project site not in the Cost Report, and expert opinion were used to allocate some costs (e.g., medical supply costs) to specific service categories.
Figure A.5.7. Allocate using local data and expert opinion.

For some costs, we did not have access to utilization data. Such costs generally account for less than 1% of total costs.
Example: Billable vaccines
Clinical experts (e.g., Director of Nursing) were asked to use locally available data and his or his expert opinion to estimate the percent of vaccines administered in different settings (e.g., primary care clinic, community settings) in order to allocate billable vaccine costs to different service categories.
Other Cost Process Information
- If a project site was not able to provide some estimates, existing data and estimates from other facilities were used.
- We used data to estimate the average cost for the five types of ECM services, home visits, and PHN clinic visits, and used the same estimates across sites.
- Once we estimated the average cost of providing each type of service, we estimated the cost of providing services for each person during the fiscal year using the service cost estimates and his or her data on service utilization.
Example: (2 primary visits * P-cost) + (1 ED visit * E-cost) = Total Cost



