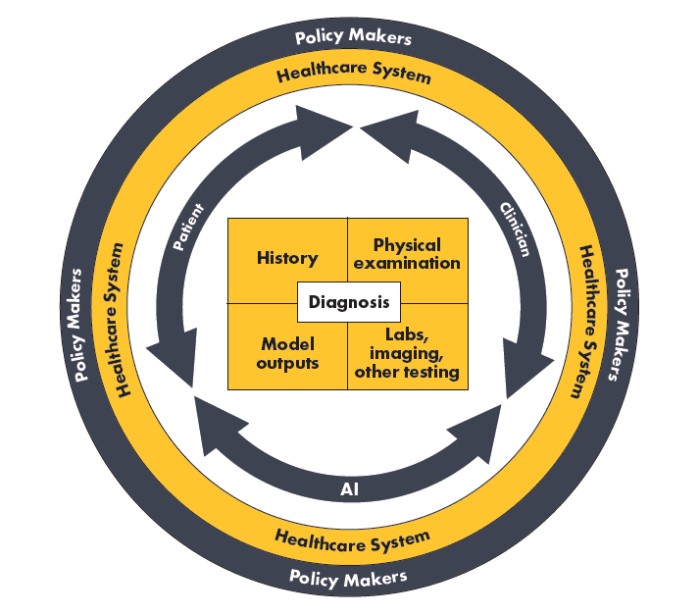
Several potential barriers must be addressed as AI algorithms are integrated into diagnostic teams. For example, liability in the event of a missed, inaccurate, or delayed diagnosis is an active area of discussion.44 In addition, payer reimbursement strategies for the use of AI algorithms in the diagnostic process are evolving. Finally, attention must be given to the potential for historically marginalized individuals to be negatively impacted by biases perpetuated by algorithms and unequal access to effective algorithms. Addressing these challenges will require engagement from all members of the diagnostic ecosystem (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Diagnostic ecosystem: factors impacting diagnostic decisions