Preventing Falls in Hospitals (Slide Presentation)
A Toolkit for Improving Quality of Care
Slide 1

Preventing Falls in Hospitals: A Toolkit for Improving Quality of Care
Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality
Toolkit: https://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/systems/long-term-care/resources/injuries/fallspx/index.html
William Spector, PhD
Slide 2

What’s New?
- Falls Prevention Toolkit for Hospitals
- Web based design
- Evidence-based tools for falls prevention (35 tools)
- Guidance for multidisciplinary change team
- Focuses on overcoming the challenges associated with developing, implementing, and sustaining a fall prevention program
- Developed by RAND Corporation, ECRI Institute, and Boston University for AHRQ
Slide 3

David Ganz, MD, PhD
RAND Corporation
Slide 4

Purpose of this project
- Develop text and tools to guide implementation and maintenance of a hospital fall prevention program
- Audience: mid-level managers and clinicians
- Coverage: all stages of organizational change
- Reference for hospital teams at different levels of sophistication
- Approaches adaptable to local circumstances
Slide 5

Toolkit/Resource Guide
- Six sections:
- Hospital readiness for change
- Managing change
- Choosing fall prevention practices
- Implementing best practices
- Measuring fall rates and fall prevention practices
- Program sustainability
Slide 6

Inputs to toolkit
- Evidence review
- Expert panel
- In person meeting + follow-up conference call
- Hospital workgroup
- Self-assessment + follow-up phone call
- In-person meeting + monthly teleconferences
- Tool evaluation forms
- Site visits
Slide 7

Hospital workgroup
- Six hospitals
- Vary on geography, safety net status, profit/non-profit, unionization, use of electronic health record
- Units selected for piloting:
- Medicine
- Neurology/neurosurgery
- Progressive care unit (telemetry/post-cath)
- Inpatient rehabilitation
- Geriatric psychiatry
Slide 8

Kathryn M. Pelczarski
ECRI Institute
Slide 9

Fall Prevention Tools
- Tailored with input from the pilot hospitals to ensure tools are:
- Realistically implementable
- Easy to use
- Broadly applicable in the acute care setting
- Highly relevant to addressing common challenges
Slide 10
Relevant Tools
Flowchart showing the following text boxes: Challenges leads to Opportunity leads to Tools That Really Help
Slide 11

Challenge
Image of Atlas holding the world on his shoulders. This depicts Atlas Syndrome (taking the burden on alone), which is unlikely to succeed.
Slide 12

Opportunity
- An interdisciplinary approach
- Essential input from key stakeholders
- Harnessing the power of collaboration
- Securing support and resources
- Gaining buy-in
- Shared ownership
Slide 13

Tool: Interdisciplinary Team (2A)
Part I: Team Members
Image of tool to list in table form the Position/Discipline, Names of Potential Implementation Team Members From Each Area, and Area of Expertise.
Slide 14
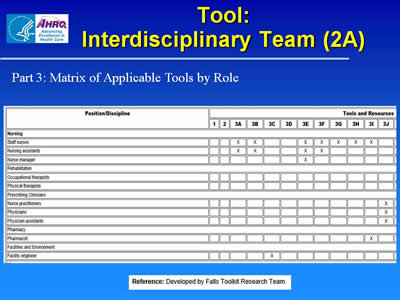
Tool: Interdisciplinary Team (2A)
Part 3: Matrix of Applicable Tools by Role
Image of tool to list in matrix form the Position/Discipline and corresponding Tools and Resources. For example, for Nurse Manager, an X is noted for Tool 3E to show that it applies to that position.
Slide 15

Tool: Action Plan (2F)
Improvement Objective: Implement standard fall prevention practices within 6 months
Image of tool in table form showing Key Interventions/Tasks, Steps To Complete Task and Tools to Use, Team Members Responsible for Task Completion, and Target Date for Completion.
Slide 16

Tool: Managing Change Checklist (2G)
Image of checklist with several tasks checked off: Implementation Team composition, Team leader identified and in place, Members with necessary expertise/role identified and invited, Team agenda and charge clearly stated, and Current state of fall prevention practice and knowledge assessed.
Slide 17

Tool: Managing Change Checklist (2G) continued
Image of checklist with additional tasks listed and Staff knowledge assessed checked off.
Slide 18

Challenge
Inadequate Risk Assessments and Reassessments
Image of young man with clipboard and image of rubber stamp
Slide 19

Opportunity
- Accurate and effective risk assessments
- Employing critical thinking and clinical judgment
- Consistency in approach
- Identifying and communicating risk at the earliest possible time
Slide 20

Tools
- Morse Fall Scale (3H)
- STRATIFY Scale (3G)
- Medication Fall Risk Scale (3I)
- Orthostatic Vital Sign Measurement (3F)
- Delirium Evaluation Bundle (3J)
Slide 21

Challenge
Inadequate and ineffective interventions
Morse Fall Score = 70
One set of interventions does not fit all
Over-reliance on bed exit alarms
Slide 22

Opportunity
- Optimizing the effectiveness of interventions
- Tailoring interventions to address individual risk factors
- Assessing their effectiveness
- Modifying interventions, as appropriate
Slide 23
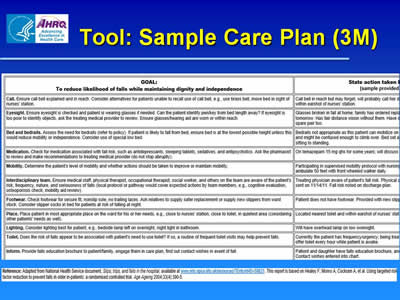
Tool: Sample Care Plan (3M)
Image of tool showing columns for goal and action taken.
Slide 24
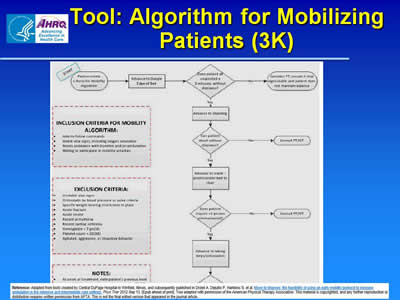
Tool: Algorithm for Mobilizing Patients (3K)
Image of flowchart for mobilizing patients, including steps to take and inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Slide 25

Challenge
Inconsistent or Ineffective rounds to address personal needs
Picture of patient lying in bed hooked up to an IV line. Pictures of items patient needs to reach: TV remote, eyeglasses, toilet, box of tissues.
Slide 26

Opportunity
- Consistent and effective rounds to address a patient’s personal needs
- Purposeful rounding
- Standardized inclusion of key elements
- Optimizing safety during rounds
Slide 27
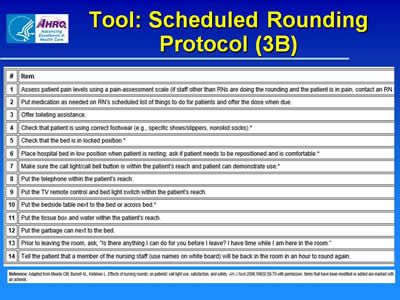
Tool: Scheduled Rounding Protocol (3B)
Image of tool showing items in protocol, such as offering toileting assistance and checking that the bed is locked.
Slide 28
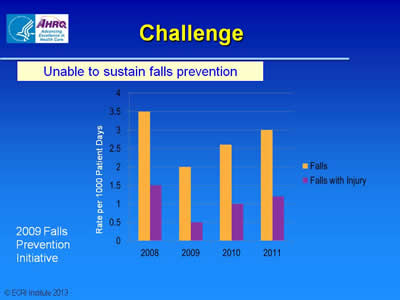
Challenge
Unable to sustain falls prevention
Graph with on falls and falls with injury. A Falls Prevention Initiative took place in 2009. Falls and falls with injury decreased from 2008 to 2009 but increased in 2010 and 2011.
Slide 29

Opportunity
- Continuous Improvement
- Identifying and addressing process challenges
- Improving compliance
- Learning from near falls and falls that do not involve harm, in addition to learning from falls with harm
Slide 30

Tools
- Assessing Fall Prevention Care Processes (5B)
- Postfall Assessment for Root Cause Analysis (3O)
- Information to Include in Incident Reports (5A)
- Measuring Progress Checklist (5C)
- Sustainability Tool (6A)
Slide 31

Tool Roadmap
Image of roadmap showing Section, Action Steps, Tool That Supports Action, and Who Should Use the Tool.
Slide 32

Pilot Hospitals
Slide 33

Charlton Memorial Hospital
Fall River, Massachusetts
Kendra Belken, PT, DPT
Physical Therapy Practice Specialist
Slide 34

Falls Knowledge Test (2E)
- Employees with various job functions in the Rehab Unit completed the test
- Tool was revised based on our input to provide more clarity in instructions and question format
- Results helped us to target education to address gaps in staff knowledge
- Environmental safety
- Medications associated with risk of falls
Slide 35

Assessing Fall Prevention Care Processes (5B)
- Tailored tool by grouping required information by location (e.g., environmental safety information in patient room, patient chart information at nurse’s station) --- reduced required audit time
- Added elements for patient room assessment (e.g., hourly rounding log complete)
- Helped monitor progress
- Plan to roll out this audit tool for use by fall prevention champions in all units
Slide 36

Augusta Health
Fishersville, Virginia
Pat Benson, BSN, RN-BC
Nursing Quality Coordinator
Slide 37

Environmental Safety Inspection List (3C)
- Added picture of typical patient room to show optimum environmental set-up corresponding to items on checklist
- Used by environmental services and nursing
Slide 38

Environmental Safety Inspection List (3C)
- Audit identified problems with bed function & provided justification for implementing bed replacement plan
- Incorporated in Post-Fall Assessment for Root Cause Analysis Tool to investigate environmental safety issues that may have contributed to patient fall
Slide 39

Thanks



