Module 2: How To Manage Change—Training Guide
Module Aim
The aim of this module is to support organizational readiness for change and to maximize the possibility of successful implementation of the Fall Prevention Program.
Module Goals
The goals of Module 2 are to identify actions needed to improve organizational readiness and maximize the chances of successfully implementing the Fall Prevention Program. The module addresses the following questions:
- How can you set up the Implementation Team for success?
- What needs to change, and how do you need to redesign practice?
- How should goals and plans for change be developed?
- How do you bring staff into the process?
Timing
This module will take 90 minutes to present.
Allow 10 minutes to present slides 1–8. That leaves 80 minutes to present and discuss the findings from Tools 2A, 2B, 2C, 2D, 2E, 2F, and 2G (slides 9–26).
Learning Methodology Checklist
- Large group discussion.
- PowerPoint slide presentation.
Materials Checklist
- LCD projector and laptop.
- “Parking lot” flip chart page (with tape or sticky band) and markers.
- Flip chart page with “Ground Rules” written at the top.
- Flip chart page with “Fall Knowledge Test” written at the top.
- Laptop computer with projection capability (optional).
Instructor Preparation
- Add the specific hospital name to the first slide.
- Meet with the Team Leader(s) before the day of training to decide how the Team will operate. Address the following questions and present the decisions during Slide 6:
Questions
- How often will the Team meet? (The recommended meeting frequency is once a week, at least in the beginning.)
- What are the ground rules for managing meeting time and communication?
- How will you communicate about progress on assignments? In person? Via email? How will the patient care Unit Team communicate with the Implementation Team?
- How will you communicate about successes?
- Ask your Information Technology (IT) Team member for ideas on how to communicate electronically between meetings to keep all Team members updated on progress.
- How will the Team do its work?
- Will you do most of your work in small groups and update everyone at the weekly meetings? Or do you plan to have working meetings?
- Alert the Implementation Team Leader(s) or designee(s) to be ready to present and discuss findings from Tools 2A, 2B, 2C, and 2D.
| Assessment Topic | Completed With Copies? Y/N |
Presenter |
|---|---|---|
| Tool 2A: Interdisciplinary Team | ||
| Tool 2B: Quality Improvement Process | ||
| Tool 2C: Current Process Analysis | ||
| Tool 2D: Assessing Current Fall Prevention Policies and Practices |
- Discuss with the Team Leader if the hospital currently uses a quality improvement (QI) change methodology, such as Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA); Lean Six Sigma (LSS); or another methodology.
- Alert the Implementation Team Leader to be ready to discuss and decide who will oversee administering the Fall Knowledge Test to staff and who will be in charge of assessing the results and folding these results into planning for staff training? (This happens during slides 19–20.)
- Have the PowerPoint file Module 2 cued on the computer and minimized.
- Have a copy of the following materials for all participants:
- Module 2 PowerPoint slide presentation handout, 3 slides to a page.
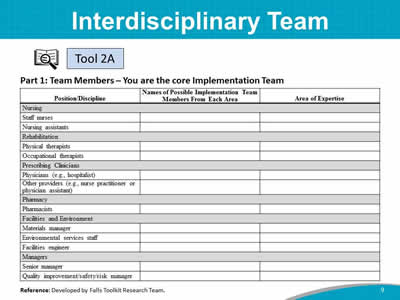
- Tool 2A: Interdisciplinary Team (completed by the Implementation Team Leader with the names and positions of those on the Implementation Team).
- Tool 2B: Quality Improvement Process (completed by the Implementation Team Leader or designee).
- Tool 2C: Current Process Analysis (completed by the Implementation Team Leader or designee).
- Tool 2D: Assessing Current Fall Prevention Policies and Practices (completed by the Implementation Team Leader).
- Tool 2E: Fall Knowledge Test.
- Tool 2F: Action Plan.
- Tool 2G: Managing Change Checklist.
Module 2: How To Manage Change
| Slide | Script |
|---|---|
|
Slide 1
|
Say: This module focuses on managing the change process, which starts with assessing the current state of fall prevention practices in your hospital. This training module covers Section 2 of the Toolkit, which addresses how to manage change. |
|
Slide 2
|
Say: The strategies used in the change process for fall prevention can also be applied to other quality improvement efforts in a hospital, such as preventing:
|
|
Slide 3
|
Say: The goals of Module 2 are to:
|
|
Slide 4
|
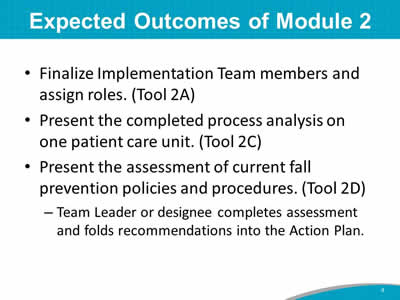
Say: The expected outcomes of Module 2 are to:
Most of the time allotted for this module centers on the assessments. Our discussion of the assessments will help identify areas that need improvement. Determining current practices is an important step in figuring out actions needed to change and improve fall prevention efforts. |
|
Slide 5
|
Say: We’ll start by identifying and prioritizing opportunities for improvement. Then we’ll draft a new or revised fall prevention Action Plan, tailored for your hospital, using Tool 2F. In this module, we will determine opportunities for Key Intervention 1: “Analyze current state of fall prevention practices in this organization in the Action Plan.” |
|
Slide 6
|
Say: Your Team Leaders met before this training to decide how the Team will operate. Instructor’s Note: Communicate the decisions the Team Leaders made. Tailor the following statements to reflect the decisions. Say:
|
|
Slide 7
|
Say: The first goal is to finalize the Implementation Team members and assign roles. |
|
Slide 8
|
Say: To accomplish the goal of implementing a successful Fall Prevention Program, an Implementation Team has:
Instructor’s Note: If the Team has a project charter that was developed and shared in Module 1, you may be able to share again who is the leadership sponsor of the project and other information on the charter. |
|
Slide 9
|
Do: Show the completed Tool 2A via computer projection, or hand out a hard copy. (Include the names of those currently in the training.) Say: (Name of Implementation Team Leader) has identified the Team members and their discipline or expertise. You are the Implementation Team. Ask: Is there anyone else you think should be on the Team? Do: Write down the names of those suggested to be added to Tool 2A. Say: Later, you can fill in other members who will be on the Team on an as-needed basis. Instructor’s Note: If you don’t already have a senior administrative manager listed, consider adding a member from the top-level hospital administration’s office. You will likely need an administrative champion to ensure there is a budget allocated for patient safety activities and to help create a hospital culture whereby patient safety is a priority. |
|
Slide 10
|
Say: A hospital quality improvement (QI) team or expert can lend tremendous expertise to the Implementation Team by helping to apply a systematic approach to the change process. The purpose of the Quality Improvement Process Tool (2B) is to link the Fall Prevention Program with your QI program. The information gleaned from the questions in this tool are intended to help you define the extent to which your hospital has resources for quality improvement. Improvement efforts tend to be most successful when teams follow a systematic QI approach to analysis and implementation, and there are multiple approaches to consider. The Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) approach, as well as other systematic approaches, are described on page 21 of the Toolkit. Ask: How do you (or have you) used the PDSA or another quality framework in your organization? Instructor’s Note: The specific type of quality improvement method/framework/tool used is not important; what matters is using a systematic approach in the change process (as noted in bullet 2 on the slide). |
|
Slide 11
|
Say: Tool 2B was developed to assess whether your organization has the needed systems in place to improve quality and performance. The Implementation Team Leader (or individual designated by the Leader) filled it out in consultation with the QI Department. The idea is to connect this fall prevention initiative with existing processes and identify opportunities for improvement to strengthen quality and performance. Ask: (Name of Team Leader), will you please share the findings from this tool with the others? Do: Have the Implementation Team Leader review the findings of Tool 2B with the group and suggest ways to link with quality improvement in the hospital. |
|
Slide 12
|
Say: As we outlined at the beginning, the second goal of this module is to work through the current process analysis of fall prevention practices in your hospital. Your Implementation Team Leader, (name), or (her/his) designee completed this task before today’s training using Tool 2C. A process analysis can help you find out what process your hospital currently uses for fall prevention. A good way to conduct a process analysis is to shadow several staff members who are completing a prevention practice and write down everything they do. A process analysis usually answers the following questions:
Once you examine and understand current prevention practices, you can assess:
|
|
Slide 13
|
Say: Here is an example of a process map from an initial patient risk assessment using the Morse Scale, done on a Medical Intensive Care Unit (ICU) in a large acute-care hospital. Several patients are admitted to the ICU directly from the Emergency Department (ED). The ED’s electronic medical record (EMR) is from a different EMR software company than the Medical ICU’s EMR. The gray boxes are the risk assessment processes. The pink boxes are where there are problems with or deviations from the processes. You will notice that the ED’s EMR does not interface with the ICU’s EMR, which creates problems in completing the risk assessment. Instructor’s Note: Point to the boxes in case participants are colorblind. Say: The process flow should not be difficult to prepare. You can use colored sticky notes, as in this example, or some other method, and work with the unit staff to identify the process. Note all the places where the risk assessment can break down. Each problem is an opportunity to be addressed in the process redesign. Also note that process analysis problems are specific to each unit, because of differences in patient population, medications, and methods on each unit. |
|
Slide 14
|
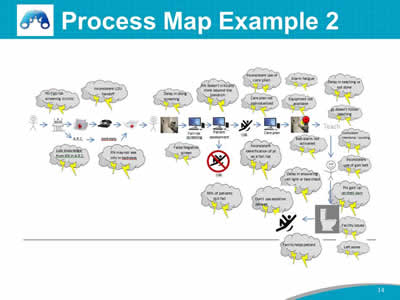
Say: This is an example of a process map from a hospital that used a Lean Six Sigma transformation approach to problem solving to help uncover opportunities to strengthen their fall prevention efforts. The Team developed a process map showing a high-level view of the steps in their fall prevention processes, from the arrival of the patient in the clinic, to the transfer to a hospital bed, fall risk screening, patient assessment, care planning, patient teaching, and then supporting the patient with mobility in the hospital. The Team identified where breakdowns, workarounds, duplication, or variation occurred at each step and indicated those using “storm clouds.” Then, the Team prioritized which steps and problems in the process to work on. |
|
Slide 15
|
Say: The Implementation Team Leader, (name), asked (names) to conduct the process analysis in your hospital. Assessment results can be compared across units to determine:
|
|
Slide 16
|
Say: (Name of the person tasked with doing the process analysis) has completed a process analysis of (patient care units). I’d like to have (him/her) describe how (he/she) mapped the key processes of fall prevention activities and then share the process mapping from these units. (He/she) will point out the key processes being used. While (name) is presenting this process analysis, please jot down notes and ideas about the process, considering:
Do: You can hand out post-it note pads to participants to jot their notes on. After the process is presented, ask for a few people to share what they noted and document their responses. Encourage participants to keep their lists handy for consideration when developing the Action Plan later in the training. Capture all responses to the above questions on the flip chart. Do: Using the computer, project the image of each process analysis, or give a hard copy of the process analysis to participants. Say: These findings will help determine which practices may need to be changed. They will also show areas where staff training may be needed. |
|
Slide 17
|
Say: The process analysis we just heard about is the flow of what and how fall prevention practices are currently conducted on the patient care units assessed. Goal 3 for the Module 2 training is to assess the written fall prevention policies and procedures of the hospital using Tool 2D. This assessment tool helps you identify what processes of care your hospital has in place and what areas need improvement. |
|
Slide 18
|
Say: (Name of the Implementation Team Leader or designee) filled out Tool 2D to assess and identify which areas need improvement. Do: Show the completed Tool 2D via computer projection, or hand out a hard copy. Say: (Name of the Implementation Team Leader or designee) identified the following policies that are in place and areas that could use improvement. You will want to address these areas in the Action Plan. Then, we will compare this assessment with best practices in Module 3. This assessment may undergo further fine tuning by your group later. (Name of Team Leader or designee), please present your findings from your assessment of the current fall prevention policies and procedures. While (name) is presenting this assessment, please jot down notes and ideas about policies and procedures, considering:
Do: After the policies/procedures are presented, ask for a few people to share what they noted and document their responses. Encourage participants to keep their lists handy for consideration when developing the Action Plan later in the training. Capture responses to the above questions on the flip chart. Say: Thank you, (name of presenter), for reviewing the assessment of the current fall prevention policies and procedures. This assessment will be very helpful when we get to Modules 3 and 4, when we will decide on best practices and then implement the best practices for a multicomponent program. |
|
Slide 19
|
Say: Another early step in the change process is to assess the current state of staff knowledge about fall prevention. Here again, we do this survey not to point out any individual staff deficiencies, but to aid in planning for training needs. Due to turnover, differences in training, and other factors, staff members will vary in their knowledge of fall prevention and treatment practices. To address these gaps through education, you need to know what the gaps are. The Fall Knowledge Test (Tool 2E) can be used to achieve this goal. Ask: Do you currently assess staff knowledge related to falls? What tools do you currently use? Say: It is recommended that you complete an assessment of staff knowledge about fall prevention. |
|
Slide 20
|
Do: Find out if the hospital uses knowledge tests/assessments and whether it is something they would find value in doing. If the Team decides not to assess knowledge, delete this slide. Say: The task today is to determine who will administer the Fall Knowledge Test and how it will be administered. The Fall Knowledge Test can be given to any health professional in the hospital but most likely will be administered to nurses and nursing assistants. The tool can be administered by a paper test collected on each patient unit or by an online test by patient unit. Collect only information about patient unit. Don’t collect staff names. Ask: Who will oversee administering the test? Who will oversee assessing the results and folding these results into planning for staff training? Instructor’s Note: The Team may elect to administer the Fall Knowledge Test to the staff on the pilot unit(s) first and then (in a stepwise fashion) administer it to other staff. Do: Write the answers to the questions on the slide or the flip chart. Share them with the staff on the pilot units. |
|
Slide 21
|
Say: Now that you have completed and discussed assessments of current policies and practices, you have an understanding of what your hospital currently does to prevent falls. These completed assessments will help you determine what should be changed in your hospital. You may already have a sense of what needs to change to decrease falls. Using the completed assessments, we will begin to identify opportunities for improvement. These opportunities can then be prioritized to develop an implementation Action Plan for your hospital’s Fall Prevention Program. The implementation Action Plan will address many areas:
|
|
Slide 22
|
Say: The implementation Action Plan also addresses:
This slide is deceptively simple. This all looks easy on paper, but it may take up to a year or so to actually get to a sustained program. |
|
Slide 23
|
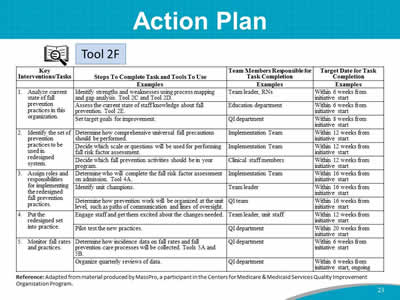
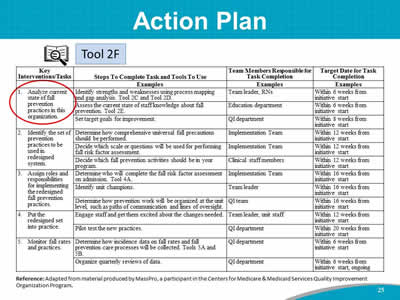
Say: We will use Tool 2F to develop your implementation Action Plan. This slide shows a sample Action Plan. Take out Tool 2F. Tool 2F lists six key tasks. For each, the Implementation Team will write in the second column the steps that will be taken to address the task, including tools to be used. In the last two columns, determine who will have lead responsibility for completing each task, and map out an estimated timeframe. The plan should guide the implementation process, and it can be continually amended and updated during the planning stages. |
|
Slide 24
|
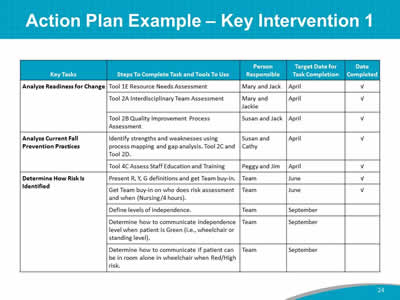
Say: Here is an example of an Action Plan for Key Intervention 1, which is “Analyze current state of fall prevention practices in this organization.” This intervention was developed by a Team like you to decrease fall incidence in a hospital. Within the first month, this hospital prevention team analyzed their hospital’s readiness for change, and they completed process mapping and gap analysis of their current prevention practices. In addition, they assessed their staff knowledge of fall prevention. Within 2 weeks or so of this training, you should have a completed draft Action Plan for the Fall Prevention Program. This plan is a living document, in that it can change as the project progresses. The completed Action Plan should be shared and discussed with the Team to obtain buy-in. |
|
Slide 25
|
Do: Start a discussion of action steps for Key Intervention 1, which is to analyze the current state of fall prevention practices in this organization. Say: Let’s take a stab at starting an Action Plan for your hospital, using the sample Action Plan as a guide. Complete as much of a draft Key Intervention 1 as possible. You may change this over the coming weeks, but let’s brainstorm some ideas that will fit into this intervention area. You have begun conducting a process analysis, and today you have been jotting down some strengths of your current processes and ideas for what may need to change. Let’s brainstorm opportunities for improvement goals. Ask: What would be the steps to complete Key Intervention 1? For example, how will you assess the current state of staff knowledge about fall prevention? Do: Write the steps as participants present them on Tool 2F or on the flip chart. Ask: Who is responsible for this task? What is a draft target date for completion of this task? Do: Write the Team member responsible and the target date for completion on Tool 2F or on the flip chart. Say: Keep Tool 2F available in your packet of information, as we will be filling out Key Interventions 2 to 5 in the upcoming modules. |
|
Slide 26
|
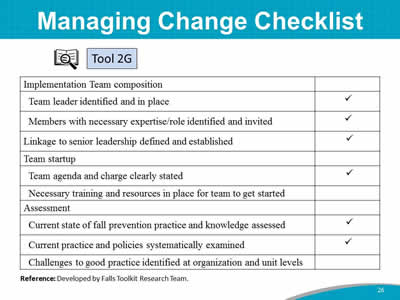
Say: To summarize what you accomplished in this training module, let’s look at Tool 2G. Here are some of the tasks you accomplished in this 90-minute module:
You accomplished a lot during this module. Let’s take a 15-minute break and then move on to Module 3. |