Catheter Utilization Ratio
Catheter utilization ratios (reflected as a percent) can be found in Figures 12, 13, 14, and 15. Ratios examined were overall utilization ratio and utilization ratio by cohort, ICU status, and bed size.
Overall
The average catheter utilization ratio when aggregating the three baseline periods (BL–BL3) was 31.3 percent. Overall, catheter utilization has remained relatively the same over the time periods; however, some variability is present (go to Table 9 for relative change over time).
Due to the project's approach of staggered cohort implementation, catheter utilization rates for later time periods do not represent the complete data for all cohorts, as only cohorts 1–3 have reached the end of the project while all remaining cohorts continue to submit data. Therefore, caution must be exercised when interpreting relative reductions in later time periods.
Figure 12. Catheter Utilization Ratio During Baseline (BL) and Post-Baseline (P) Collection Periods – (Catheter Days/Patient Days)
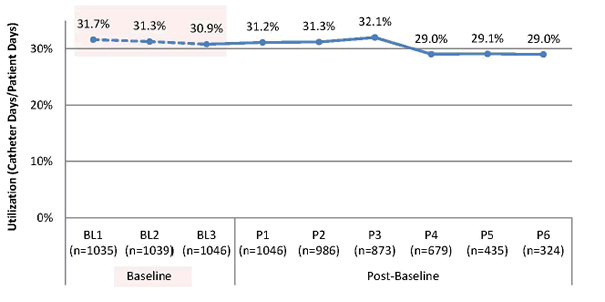
Note: n's represent the total number of reporting units for corresponding collection periods.
Table 9. Relative Change From Baselinea
| Post-Baseline Collection Periods | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Units Reporting | 1,046 | 986 | 873 | 679 | 435 | 324 |
| Utilization Ratio |
31% | 31% | 32% | 29% | 29% | 29% |
| Relative Change |
-0.3% | -0.1% | 2.5% | -7.2% | -7.0% | -7.3% |
a. Baseline aggregated over three baseline time periods (BL1–BL3).
Cohort Status
Figure 13. Catheter Utilization Ratio During Baseline (BL) and Post-Baseline (P) Collection Periods – By Cohort Status – (Catheter Days/Patient Days)
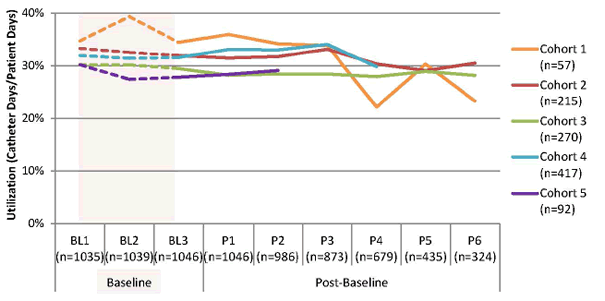
Note: n's represent the total number of reporting units for corresponding cohorts and collection periods.
ICU Status
Figure 14. Catheter Utilization Ratio During Baseline (BL) and Post-Baseline (P) Collection Periods – By ICU Status – (Catheter Days/Patient Days)
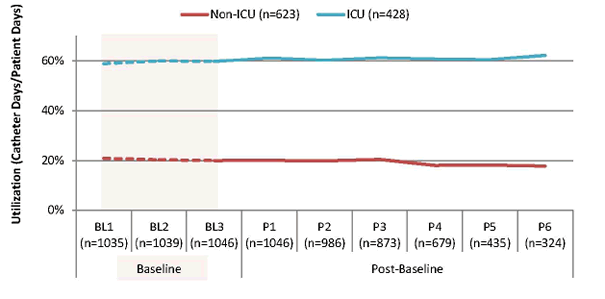
Note: n's represent the total number of reporting units for corresponding unit types and collection periods.
Bed Size
Figure 15. Catheter Utilization Ratio During Baseline (BL) and Post-Baseline (P) Collection Periods – By Bed Size – (Catheter Days/Patient Days)
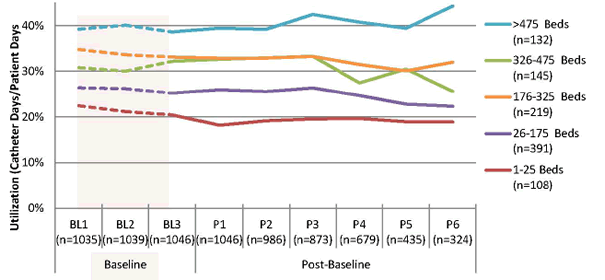
Note: n's represent the total number of reporting units for corresponding bed sizes and collection periods.
Culture Measures
Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture
The Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture (HSOPS) is a reliable and valid survey6 designed to assess clinician and staff perceptions of the culture of safety within their unit and overall hospital. The instrument contains seven unit-level safety culture dimensions, four hospital-level dimensions, and four outcome variables. To date we have collected over 700 baseline surveys, representing 56 percent of participating units, and over 300 followup surveys, representing 24 percent of participating units.
Team Checkup Tool
Participating units were requested to complete a Team Checkup Tool (TCT) evaluating three primary domains: adoption of CUSP activities, implementation of CAUTI reduction steps, and progress barriers. While HSOPS is a validated survey looking at hospital safety improvements both before and after intervention, the TCT is designed to keep patient safety culture front and center at both the system and unit level. This is accomplished by the team working through the tool to identify common barriers, thereby providing the awareness and information needed to address issues related to patient safety barriers. TCTs are to be completed and submitted by unit teams quarterly throughout project participation. Currently, 628 TCTs have been completed across five cohorts, representing less than 60 percent of participating teams. Ongoing efforts continue to increase both HSOPS and TCT data submission. Future analyses will be conducted with increased submissions.
6. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. "Safety Culture Dimensions and Reliabilities." User's Guide: Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture. AHRQ Publication No. 04-0041. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. September 2004. http://www.ahrq.gov/professionals/quality-patient-safety/patientsafetyculture/hospital/userguide/hospdim.html



