What Is Patient Safety Culture?
Patient Safety Culture Defined
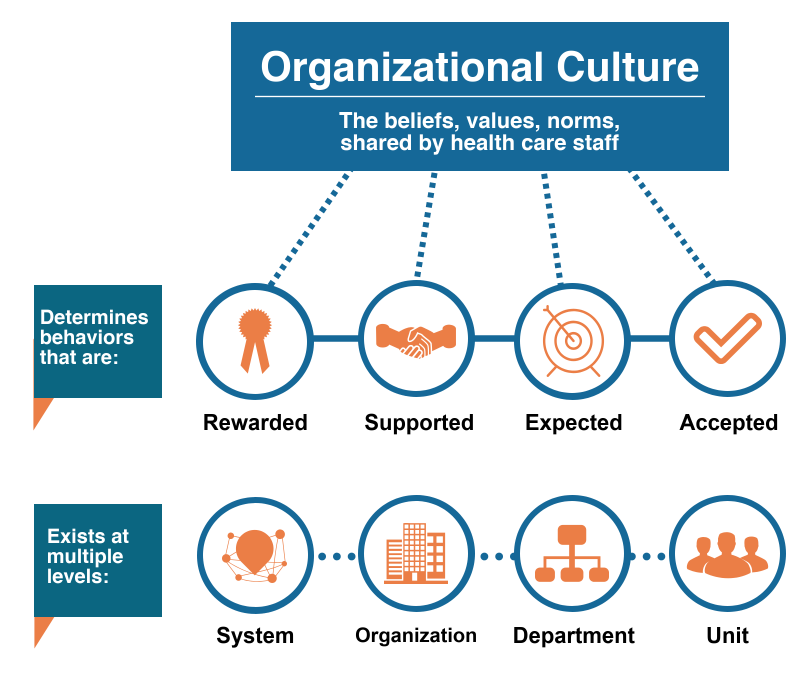
Patient safety culture is the extent to which an organization's culture supports and promotes patient safety. It refers to the values, beliefs, and norms that are shared by healthcare practitioners and other staff throughout the organization that influence their actions and behaviors. Patient safety culture can be measured by determining the values, beliefs, norms, and behaviors related to patient safety that are rewarded, supported, expected, and accepted in an organization. It is also important to note that culture exists at multiple levels, from the unit level to the department, organization, and system levels.
SOPS Surveys Measure Patient Safety Culture
The AHRQ Surveys on Patient Safety Culture® (SOPS®) Program develops and supports surveys of providers and staff that assess the extent to which their organizational culture supports patient safety and safe practices. All of the SOPS surveys include a standard set of core items with comparable survey content across facilities. SOPS surveys have been developed for the following settings of care:
- Hospitals.
- Medical Offices.
- Nursing Homes.
- Community Pharmacies.
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers.
The SOPS Program also offers optional supplemental item sets that can be added to the core surveys to assess additional content areas focusing on health information technology patient safety, workplace safety, value and efficiency, and diagnostic safety.
SOPS surveys and supplemental item sets undergo a rigorous development and testing process. Because the surveys ask questions that have been developed and pilot tested using a consistent methodology across a large sample of respondents, they are standardized and validated measures of patient safety culture.
Areas of Patient Safety Culture Assessed by the SOPS Surveys
The areas of patient safety culture assessed by the AHRQ SOPS surveys include:
- Communication About Error.
- Communication Openness.
- Organizational Learning—Continuous Improvement.
- Overall Rating on Patient Safety.
- Response to Error.
- Staffing.
- Supervisor and Management Support for Patient Safety.
- Teamwork.
- Work Pressure and Pace.
Each of these areas is assessed by multiple survey items to enable reliable measurement and facilitate patient safety culture improvement efforts. In addition, survey items are customized for each setting of care.
Relating SOPS Patient Safety Culture Survey Data to Outcomes
Research has shown that significant relationships exist between SOPS patient safety culture scores and important healthcare delivery measures and outcomes. Some key findings based on studies that administered SOPS surveys include the following:
- Hospital units with more positive SOPS scores had:
- Hospitals with more positive SOPS scores had:
- Nursing homes with more positive SOPS scores had:
Learn more: Explore the SOPS bibliography to browse or search for publications about the use of SOPS surveys.
References:
- Brown DS, Wolosin R. Safety culture relationships with hospital nursing sensitive metrics. J Healthc Qual. 2013 Jul-Aug;35(4):61-74. doi: 10.1111/jhq.12016.
- Fan CJ, Pawlik TM, Daniels T, Vernon N, Banks K, Westby P, Wick EC, Sexton JB, Makary MA. Association of safety culture with surgical site infection outcomes. J Am Coll Surg. 2016 Feb;222(2):122-8. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26712245/.
- Mardon RE, Khanna K, Sorra J, Dyer N, Famolaro T. Exploring relationships between hospital patient safety culture and adverse events. J Patient Saf. 2010 Dec;6(4):226-32. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0b013e3181fd1a00.
- Sorra J, Khanna K, Dyer N, Mardon R, Famolaro T. Exploring relationships between patient safety culture and patients’ assessments of hospital care. J Patient Saf. 2012 Sep;8(3):131-9. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0b013e318258ca46.
- Yount N, Zebrak KA, Famolaro T, Sorra J, Birch R. Linking patient safety culture to quality ratings in the nursing home setting. J Appl Gerontol. 2022;41(1):73-81. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33158388/.
- Abusalem S, Polivka B, Coty M, Crawford TN, Furman CD, Alaradi M. The relationship between culture of safety and rate of adverse events in long-term care facilities. J Patient Saf. 2021;17(4):299-304. doi: 10.1097/PTS.0000000000000587.



