Module 4: How To Implement the Fall Prevention Program in Your Organization—Slide Presentation
Slide 1: How To Implement the Fall Prevention Program in Your Organization

ADD Hospital Name Here
Module 4
Slide 2: What We Have Done Thus Far

Up to this point, you have:
- Examined compelling reasons for implementing a Fall Prevention Program and strategies for sustaining effective practices (Module 1).
- Identified current practices and aspects needing improvement (Module 2).
- Identified best practices and made preliminary decisions on what best practices will be included in your Fall Prevention Program (Module 3).
Slide 3: Following Best Practice

In this module, the Implementation Team will plan for implementation of new/modified prevention practices at the clinical care level.
Image: Photograph shows medical providers holding a meeting next to a laptop.
Slide 4: Implementation Planning Goals

- Determine the role/responsibilities of staff in preventing falls.
- What role will the Unit Team play?
- What role will the Unit Champions play?
- How should prevention work be organized at the unit level?
- What fall prevention practices go beyond the unit?
Slide 5: Implementation Planning Goals

- Put the new practices into operation.
- How do you manage the change process at the patient care level?
- How do you pilot test the new practices?
- How do you get staff engaged and excited about fall prevention?
- How can you help staff learn new practices?
Image: Photograph shows medical providers at patient’s bedside.
Slide 6: Staff Roles

Assign staff to perform each specific task in your set of best practices, based on training and experience.
Images: Two photographs show medical providers with clipboards and looking at a computer screen.
Slide 7: Staff Roles

- In some cases, a group will perform the task based on specific roles, such as the nursing assistants.
- Other tasks may be assigned to a specific person.
- In that case, be sure to assign a backup person.
Image: Photograph shows a medical provider assisting a patient with a mobility device.
Slide 8: Best Practices

Images: Instructions and a table for Assigning Responsibilities for Using Best Practices is shown. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book identifies this as Tool 4A.
Slide 9: Staff Roles

Images: Three photographs show a medical provider looking at a tablet, a medical provider standing at a patient’s bedside, and a medical provider holding on to a patient doing physical therapy.
Slide 10: Staff Roles

Examples of how responsibilities may be assigned.
Images: Two screenshots show a sample table assigning roles to staff members. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book identifies this as Tool 4B.
Slide 11: Unit Team

A Unit Team comprises staff members who provide daily direct patient care by:
- Conducting fall risk assessments.
- Planning care for fall prevention.
- Ensuring care is performed and documented.
Image: Photograph shows medical providers and family members at a patient’s bedside.
Slide 12: Unit Team

- A Unit Team is composed of those who provide daily direct care:
- Nurse.
- Nurse assistant.
- Treating medical provider.
- Pharmacist.
- Physical or occupational therapist.
- Other staff assigned to the unit on a regular basis.
- Patient and family.
Image: A collage of photographs shows medical providers holding meetings, assisting a patient with a mobility device, standing with family member at a patient's bedside, writing at a desk, and holding a tablet. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book refers to Page 55.
Slide 13: Staff Turnover

All hospitals experience the challenges of staff turnover.
Image: Photograph shows medical providers looking in a folder.
Slide 14: Practice Insight

Staff Turnover
Image: Icon of binoculars.
Slide 15: Unit Champion

- Staff member who serves as the liaison between the Implementation Team and the unit staff.
- Most familiar with the program goals, care processes, and outcome data to be used.
- Critical during the implementation process (may be temporary).
- Ideally, one champion per shift, per unit.
Slide 16: Communication During Implementation

Staff at all levels need to communicate.
- Within the unit—among nurses, nurses and assistants, nurses and physicians, and nurses and patients and their families.
- Among unit staff, the Implementation Team, and senior management
Image: Three photographs show medical providers looking at papers, holding a staff meeting, and looking at a computer screen.
Slide 17: Communication During Implementation

- Develop a communication process to share information about the effectiveness of implemented changes.
- Unit Champions can present updates on implementation at regularly scheduled meetings.
- Updates can be given thoroughly and succinctly with the least amount of time and effort.
Slide 18: Integrate Into Ongoing Processes

- Necessary for sustainability.
- Universal fall precautions.
- Integrated into regular communications (e.g., shift handoffs).
- Use of visual cues/logos (e.g., sign above patient’s bed noting need for assistance with toileting).
Image: Photograph shows a medical provider with a commode at patient’s bedside. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book refers to Page 58.
Slide 19: Electronic Health Record

- What information about fall risk factors is already part of the patient record?
- What is the most logical place in the record to collect, organize, and assess information about patient fall risk factors and any necessary precautions?
Image: Photograph shows a medical provider with a tablet at a patient’s bedside. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book refers to Page 59.
Slide 20: Manage the Change Process

- Ensure staff understand new roles.
- Ensure staff understand reasons for change and agree change is needed.
- Convey that fall prevention is part of high-quality care, and it is valued by all, including senior hospital leadership.
Slide 21: Manage the Change Process

- Have adequate access to supplies and equipment available.
- Assistive devices.
- Low beds.
- Floor mats.
- Engage staff to gain support and buy-in to tailor new practices.
Image: Photograph shows medical providers using gait belt with a patient.
Slide 22: Monitor Implementation Progress

- Baseline measures of fall rates and processes should be obtained before any change.
- Tracking care processes to prevent falls is a measure of implementation success, and it should translate into better outcomes.
- Outcome measures—track changes in fall rates.
- Inform the Implementation Team and staff about results.
Slide 23: Communicate Success

- Tips for how to convey updates and information on successes from prevention activities include using:
- Posters with results on the units or in the lunch room.
- Storyboards highlighting successes.
- Newsletter articles.
- Email blasts.
- Announcements on the hospital home page.
- Discussions during staff meetings.
Slide 24: Sustain Fall Prevention

- Close the information loop. Inform senior leaders and middle managers about progress.
- Keep clinical staff informed about progress with the Fall Prevention Program.
Image: Photograph shows a medical provider giviing a presentation.
Slide 25: Staff Education and Training

- Develop an education plan.
- Adults learn best through experiential activities.
- Don’t forget prevention education for the patient, family members, and significant others.
Image: An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book sits above the text "See Tool 3L."
Slide 26: Practice Insight

Frontline Staff Training/Coaching
Image: Icon of binoculars.
Slide 27: Staff Education and Training

- Regular/ongoing education means including fall prevention in four areas of training:
- Annual fall prevention education for all staff.
- Staff competencies.
- New staff orientation.
- Training of temporary staff.
Image: Photograph shows staff members at training.
Slide 28: Assess Staff Education
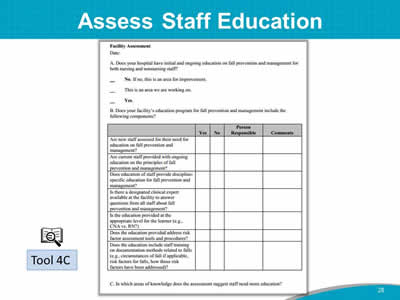
Images: A screenshot shows a sample Facility Assessment tool. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book identifies this as Tool 4C.
Slide 29: Action Plan

- Action steps for Key Interventions 3 and 4.
- Who is responsible for these tasks, and when will they be completed?
Images: A sample Action Plan is shown with Key Interventions 3 and 4 circled in red. An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book sits above the text "Refer to your Action Plan."
Slide 30: Summary

Image: A sample Implementing Best Practices checklist is shown in table form. The checklist items are:
- Roles and Responsibilities of Staff.
- Assign specific roles and responsibilities to:
- Members of the Unit Team.
- Unit Champion.
- Organizing the Prevention Work.
- Identify paths of ongoing communication and reporting.
- Develop mechanisms to address accountability.
- Identify strategies for building new practices into daily routine.
- Refine preliminary implementation plan.
- Ensure support from key stakeholders.
- Initiate plan to pilot test new practices.
- Establish strategy for engaging staff.
- Create education plans to help staff learn new practices.
An icon of a magnifying glass in front of open book identifies the checklist as Tool 4D.



