Preventing CAUTI in Specialized Patient Populations: The ICU
Slide Presentation
Slide 1

Preventing CAUTI in Specialized Patient Populations: The ICU
Hannah Wunsch, MD, MSc
Herbert Irving Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology and Epidemiology
Columbia University
Eugene Chu, MD, FHM
Director of Hospital Medicine
Boulder Community Hospital
Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine
University of Colorado School of Medicine
Images: Photos of the 2 presenters.
Slide 2

Additional Presenters
University Medical Center of Southern Nevada
Las Vegas, NV
Marlon Medina BSN, RN
Ashley E. Komacsar BSN, RN
Images: Photos of the 2 additional presenters.
Slide 3

Learning Objectives
- Describe the relationship between culture change and CAUTI reduction
- Understand the CUSP framework for initiating culture change
- Apply culture change theory to urinary catheter culture
- Articulate the barriers to CAUTI reduction in the ICU population:
- Understand unique barriers in the ICU population
- Compare reduction of CAUTIs with other similar issues in the care of ICU populations
- Recognize the value in using incentives to change behavior regarding catheter use in the ICU:
- Using positive incentives to change behavior in regard to catheter use in the ICU
- Catheter alternatives, nurse education, and engaging leadership
Slide 4

On the CUSP: Stop CAUTI
Culture Change: The 4 E’s and the Elephant
Slide 5

Case
Image: Photo of an older woman.
Slide 6

What is the cause of Ms. B’s hypoxia?
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Acute coronary syndrome with CHF
- Pneumothorax
- Pulmonary embolism
Image: Same photo as the one in Slide 5.
Slide 7

What is the cause of Ms. B’s hypoxia?
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Acute coronary syndrome with CHF
- Pneumothorax
- Pulmonary embolism
Image: Same photo as the one in Slide 5.
Slide 8
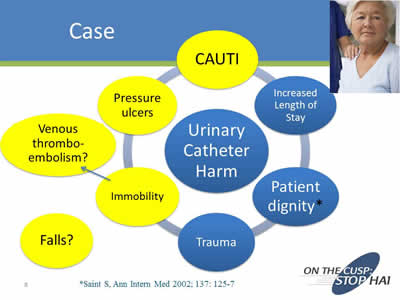
Case
Image: Diagram showing the causes of urinary catheter harm.
*Saint S, Ann Intern Med 2002;137:125-7
Image; Same photo from Slide 5 on top right side in smaller size.
Slide 9
Aims
- Understand the CUSP framework for initiating culture change
- Apply culture change theory to urinary catheter culture
Slide 10

Organizational Culture
…the shared set of social values and beliefs, both explicit and implicit, that guides actions and decisions within the organization
Slide 11
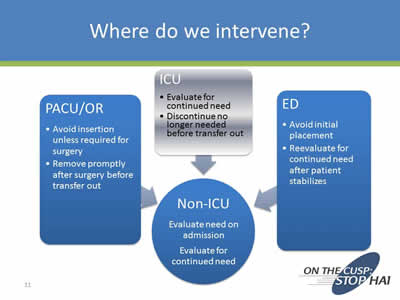
Where do we intervene?
Image: Diagram with the following text:
PACU/OR
- Avoid insertion unless required for surgery
- Remove promptly after surgery before transfer out
ICU
- Evaluate for continued need
- Discontinue no longer needed before transfer out
ED
- Avoid initial placement
- Reevaluate for continued need after patient stabilizes
PACU/OR, ICU, and ED all point to:
Non-ICU
- Evaluate need on admission
- Evaluate for continued need
Slide 12

CAUTI ICU Culture
CAUTI
Indications
- Orders
- HICPAC
Insertion and Maintenance
- Technique
- Competency
Removal
- Process
- Structure
Image: Urinary catheter with a large red circle with a line inside superimposed over it.
Slide 13

Leading Change
For anything to change, someone has to start acting differently.
Image: Book cover for a book titled: "Switch: How to Change When Change is Hard".
Slide 14

Images: The book cover in the slide above, the CUSP logo, and the book cover for "Leading Change" by John P. Kotter.
Slide 15

Changing Patient Safety Culture
| Senior Leaders | Team Leaders | Staff | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engage | How does this make the world a better place? | ||
| Educate | What do we need to do? | ||
| Execute | What keeps me from doing it?
How can we do it with my resources? |
||
| Evaluate | How do we know we improved safety? | ||
Slide 16

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Drawing of a man riding an elephant. To the left of the drawing it says "individual". To the right it says "direct the rider", "motivate the elephant", and "shape the path. Bottom left are the book covers of "Switch" and "The Happiness Hypothesis".
Slide 17

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 16, only on the left instead of individual, is says "organization".
Slide 18

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 17, only on the left instead of individual, it says "society".
Slide 19

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 18, only on the left instead of individual, it says "educate, engage, and execute and evaluate" and the CUSP logo is also displayed.
Slide 20
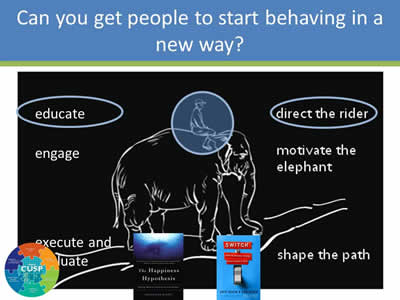
Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 19, only the elephant rider is circled, the word educate is circled, and so are the words "direct the rider".
Slide 21
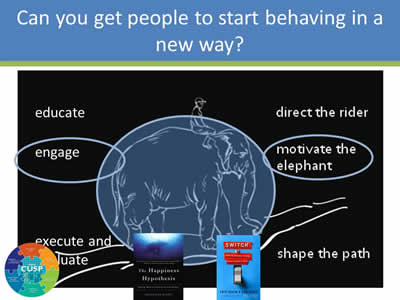
Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 19, only the elephant is circled, the word "engage" is circled, and so are the words "motivate the elephant".
Slide 22

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 20, only the words "execute and evaluate" are circled, and so are the words "shape te path".
Slide 23

Population Health Improvement
Image: The outline of the state of West Virginia with a photo of some scenery inside.
Slide 24

Eat Healthy!
Images: The Get Healthy Food Pyramid and a healthy eating food plan.
Slide 25

Use Skim Milk!
Images: Gallon jugs of skim and whole milk.
Slide 26

Images: Same image as Slide 25, only there are 2 additional dishes of butter shown.
Slide 27

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 20, plus an image of a gallon of skim milk, the book cover for "Switch", the words Educate: What do we need to do? and the CUSP logo. Also underneath the elephant drawing is the phrase "What looks like resistance is often a lack of clarity".
Slide 28
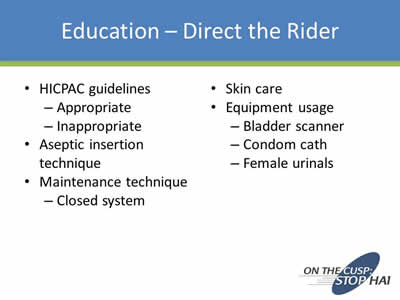
Education – Direct the Rider
- HICPAC guidelines:
- Appropriate
- Inappropriate
- Aseptic insertion technique
- Maintenance technique:
- Closed system
- Skin care
- Equipment usage:
- Bladder scanner
- Condom cath
- Female urinals
Slide 29

Taste Test
Images: Photos of a bunch of radishes and a plate of chocolate chip cookies.
Slide 30

Which group attempted the puzzle for a longer time before giving up?
- The group that could eat the cookies
- The group that could only eat the radishes
- No difference
Images: Photos of a bunch of radishes and a plate of chocolate chip cookies.
Slide 31

Which group attempted the puzzle for a longer time before giving up?
- The group that could eat the cookies
- The group that could only eat the radishes
- No difference
Images: Photos of a bunch of radishes and a plate of chocolate chip cookies.
Slide 32

Can You Get People to Start Behaving in a New Way?
Image: Same image as Slide 21, but instead of the words on the left there is plate of cookies. Under the image of the elephant is the phrase "What looks like laziness is often exhaustion."
Slide 33

Engage – Patients
Image: Photo an an elderly woman superimposed over the causes of CAUTI.
*Saint S, Ann Intern Med 2002; 137:125-7
Slide 34
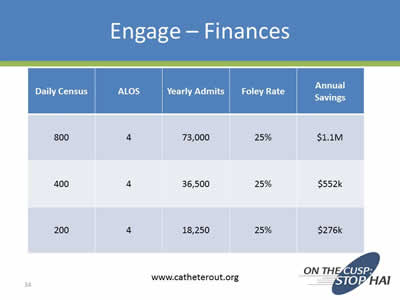
Engage – Finances
| Daily Census | ALOS | Yearly Admits | Foley Rates | Annual Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 800 | 4 | 73,000 | 25% | $1.1 M |
| 400 | 4 | 36,500 | 25% | $552K |
| 200 | 4 | 18,250 | 25% | $276K |
www.catheterout.org
Slide 35

Engage – Vision
- Imaginable
- Feasible
- Desirable
- Focused
- Flexible
- Communicable
Images: Catheter with a large red circle with a line through it superimposed over it, and the book cover for "Leading Change" by John P. Kotter.
Slide 36

Don't Forget the Cookies
Image: A plate of chocolate chip cookies.
Slide 37

Free Popcorn
Images: Photo of a pile of popcorn and the promo for the movie "Payback" with Mel Gibson.
Slide 38

What characteristics were different between the groups?
- Age
- Gender
- BMI
- All of the above
- None of the above
Images: Same images as in Slide 37.
Slide 39

What characteristics were different between the groups?
- Age
- Gender
- BMI
- All of the above
- None of the above
Images: Same images as in Slide 37.
Slide 40

Images: Drawing of a man riding an elephant only the path is circled, and so are the words "shape the path". Underneath the drawing is the phrase "What looks like a people problem is often a situation problem". To the left of the drawing is a photo of 4 large bucks of popcorn, the book cover for the book "Switch", and below is that is the Execute and Evaluate rows from the table in Slide 15.
Slide 41
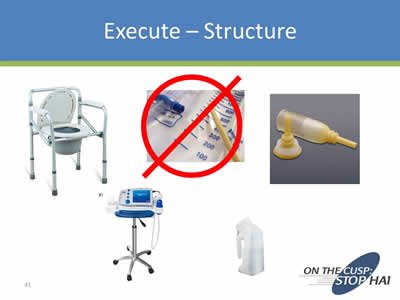
Execute – Structure
Images: Photo a urinary catheter with a red circle and a line through it, plus images of catheter alternatives.
Slide 42

Execute – Processes
- Orders with indications
- Nurse driven removal protocol
- Acute urinary retention protocol
- Insertion and maintenance competency evaluations
- ED and OR -> ICU processes
- Monitoring and Feedback
Slide 43

Evaluation
- Use data to assess progress:
- Hospital Survey on Patient Safety
- Infection rates
- Process measures
- Organizational and team culture
Slide 44

Image: Same image as Slide 16, only without the word "individual" on the top left.
Slide 45

Organizational Culture
…the shared set of social values and beliefs, both explicit and implicit, that guides actions and decisions within the organization
Slide 46

CAUTI ICU Culture
CAUTI
Indications
- Orders
- HICPAC
Insertion and Maintenance
- Technique
- Competency
Removal
- Process
- Structure
Image: Urinary catheter with a large red circle with a line inside superimposed over it.
Slide 47

Learning Objectives
- Understand unique barriers in the ICU population
- Compare reduction of CAUTIs with other similar issues in the care of ICU populations
Slide 48
Last patient of the morning (11:45 a.m.)
- 75 yo M
- Hx of HTN, DM2
- Admitted 24 hours earlier “for monitoring” after a pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple)
- Doing well, good UOP, no vasopressors
Would you remove the urinary catheter as part of your plan for the day?
Slide 49

Why do ICU patients feel ‘special’?
- “If you touch them they desaturate”
- “They are on high doses of vasopressors and their kidney function is tenuous”
- “They are at high risk for a sacral decub”
- “They are at risk for abdominal compartment syndrome and I’m monitoring UOP”
- They are “sick” and we need to know “ins and outs” every hour
The need for urinary catheters in the ICU will never go away
Slide 50

So why is it so hard to change things?
- What is YOUR biggest barrier?
- The nurse/physicians in the unit want to take the Foley out, but the surgeon/oncologist also caring for the patient wants it in
- Everyone still wants ‘ins and outs’ every hour
- There are so many other things to discuss on rounds
Slide 51

So why is it so hard to change things?
- What is your biggest barrier?
- The nurse/physicians in the unit want to take the Foley out, but the surgeon/oncologist also caring for the patient wants it in
- Everyone still wants ‘ins and outs’ every hour
- There are so many other things to discuss on rounds
Slide 52

ICU care is complex even in a ‘closed’ unit
- ICU:
- Intensivist
- Pharmacist
- Respiratory therapist
- Nurse
- Surgeon
- Infectious disease specialist
- (Resident)
- Emergency medicine
- EM physician
- Nurse
Slide 53
Time frame
- Time for care in the ED is short
- Time for care in the ICU is long
Slide 54

So why is it so hard to change things?
- What is your biggest barrier?
- The nurse/physicians in the unit want to take the Foley out, but the surgeon/oncologist also caring for the patient wants it in
- Everyone still wants ‘ins and outs’ every hour
- There are so many other things to discuss on rounds
Slide 55

It used to be…
- ‘everyone still wants a wedge pressure on every sick patient’
Image: Photo of a catheter.
Slide 56
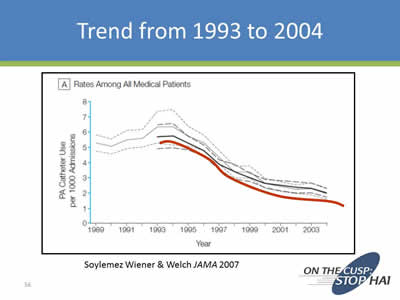
Trend from 1993 to 2004
Image: Line chart showing a decrease in catheter use per 1000 hospital admissions. Source: Soylemez Wiener & Welch JAMA 2007.
Slide 57
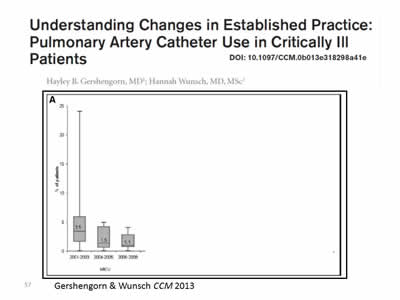
Image: Plot graph from journal article titled: "Understanding Changes in Established Practice: Pulmonary Artery Catheter Use in Critically Ill Patients". Source: Gershengorn & Wunsch CCM 2013.
Slide 58
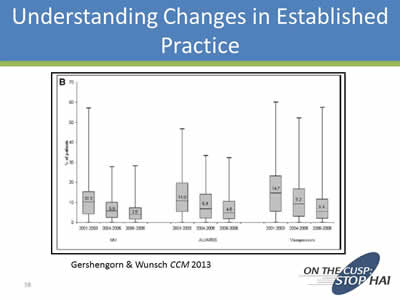
Understanding Changes in Established Practice
Image: Plot graph showing decreases in various catheter usages from 2001-2003, 2004-2005, and 2006-2008. Source: Gershengorn & Wunsch CCM 2013.
Slide 59
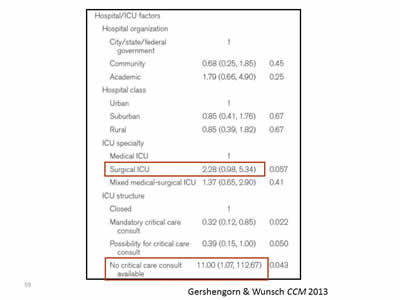
Image: Screen shot of table from the Gershengorn & Wunsch CCM 2013 journal article. The data for Surgical ICU and No critical care consult available is highlighted.
Slide 60

So why is it so hard to change things?
- What is YOUR biggest barrier?
- The nurse/physicians in the unit want to take the Foley out, but the surgeon/oncologist also caring for the patient wants it in
- Everyone still wants ‘ins and outs’ every hour
- There are so many other things to discuss on rounds
Slide 61

Back to the 4Es (Sort Of)
- Engage
- Educate
****Empower ***** - Execute
****Celebrate***** - (Evaluate)
Slide 62

A Lot of People - And You Only Need One
- Nurse
- Pharmacist
- Physical Therapist
- Respiratory Therapist
- PA
- NP
- Fellow
- Resident
- Medical Student
Slide 63

Example of Empowerment
Image: Photo of janitor mopping a hospital floor.
Slide 64

ICU Is a Lot of ‘Doing’
- Place the Foley
- Place the central line
- Monitor Ins and Outs
- Place the arterial line
- Send off the ABG
- Intubate
- Change the ventilator settings
- Order another test
Slide 65

Human Nature
Linda Lewis
"Don't just do something, stand there"
Image: Photo of Linda Lewis behind quote bar.
Slide 66

Celebrate the ‘Removal’
Image: Photo of exploding fireworks.
Slide 67

On the CUSP: Stop CAUTI
A Journey to Prevent CAUTI & Improve Patient Safety in the ICU
University Medical Center of Southern Nevada
Las Vegas, NV
Marlon Medina BSN, RN
Ashley E. Komacsar BSN, RN
Images: Photos of the 2 presenters.
Slide 68
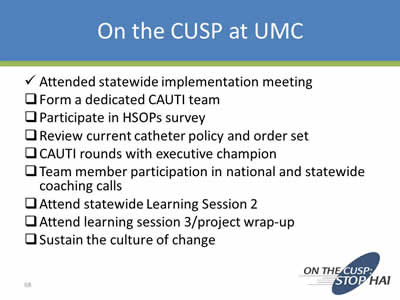
On the CUSP at UMC
✓ Attended statewide implementation meeting
__ Form a dedicated CAUTI team
__ Participate in HSOPs survey
__ Review current catheter policy and order set
__ CAUTI rounds with executive champion
__ Team member participation in national and statewide coaching calls
__ Attend statewide Learning Session 2
__ Attend learning session 3/project wrap-up
__ Sustain the culture of change
Slide 69

Formation of CAUTI Team
- Unit Manager:
- For support, leadership, & time allocation
- Unit Charge Nurses:
- For support, consistency, resource, & data collection
- Unit Team Leader:
- Peer champion, coordinate project efforts, staff empowerment
- Staff Nurses:
- Heart of operation, implement CUSP at the bedside
- Infection Control:
- Data collection & submission, coordination of house-wide efforts
- Physician Champion:
- Support change at physician level, coordinate multidisciplinary care
- Executive Champion:
- Administrative support, allocation of resources
Slide 70

Review of Policy & Practice 2012
- Physician Foley Daily Order Form:
- Physician to order Foley with approved indication
- Physician to assess daily if catheter meets indication
- Daily Bundle Checklist:
- Daily tasks for best practice (i.e. Bag below bladder, use of securement device, seal not broken)
- Nurse to complete when care on sheet is completed
Slide 71

Executive Champion CAUTI Rounds
- Our Chief Financial Officer & Executive Champion was invited to round on the unit
- Explanation of CUSP given
- A chance to interact with staff and voice safety concerns
- Attended Bard catheter training class with CAUTI team members
Slide 72

Team Member Participation
- National Content Calls:
- Tuesdays once monthly
- Different and guest speakers present information on various areas within CUSP
- State Coaching Calls:
- Once monthly
- State data shared
- A chance for hospitals to network and exchange progress and offer assistance
- CAUTI Team Unit Meetings:
- Quarterly
- Perform analysis of CAUTI incidents
- Reflect on state and national content
- Brainstorm and implementation of projects within unit
Slide 73

Learning Session 2 & 3
- April 16, 2013 in Reno, NV
- Presentations from Nevada hospitals:
- Saint Mary’s, Renown, Tahoe Pacific
- Identifying Barriers:
- Education, Increased Workload, Participation, Resources, Foley Alternatives
- Learning from Defects
- Prevention Strategies
- Culture Change & Sustainment
- Teamwork in Action
- Team Sharing and Action Plan
- Staff Safety Assessment Discussion
- February 7, 2014 in Reno, NV
- Project wrap-up and final data presentation
- Sharing greatest successes & barriers
- Culture Sustainment
- Awards Presentation
Image: Photo of the award presented to the University Medical Center of Southern Nevada Neurosurgical Critical Care Unit in 2013.
Slide 74

On the CUSP in Action
- Changes on NSCU:
- CUSP Information boards assembled
- Foley Decision tree in every room
- Development of CAUTI Alert
- Increased staff vigilance and catheter removal
- Continued attendance of calls and regular meetings
- House-Wide Changes:
- Bard sponsored Foley Catheter Class & new departmental testing
- Providing and utilizing more Catheter Alternatives
- Change in stocking of urinary catheter trays
- Revision/Update of Foley policy
- Nurse-Driven Foley removal
Slide 75

CUSP Information Boards
- First CUSP project for NSCU
- Created after CUSP implementation
- Provides information on CUSP
- Provides information on CAUTI
- Used to engage staff, physicians, & family in unit project
Image: Photo of an On the CUSP information board.
Slide 76
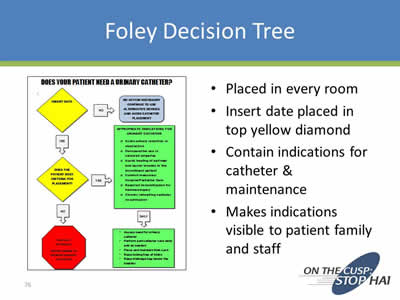
Foley Decision Tree
- Placed in every room
- Insert date placed in top yellow diamond
- Contain indications for catheter & maintenance
- Makes indications visible to patient family and staff
Image: Screen shot of a Foley Decision Tree titled "Does Your Patient Need A Urinary Catheter?"
Slide 77

CAUTI Alert
- Tool to alert staff of a CAUTI
- Lists date & time of event
- Cites NHSN criteria for event labeled as a CAUTI
- Raises awareness of incident for use for further prevention
Image: Screen shot of a sample CAUTI alert report.
Slide 78

Foley Catheter Training
- Bard was invited to provide classes reviewing the product and current insertion and maintenance techniques
- UMC department of Clinical Research & Education put together a departmental test placed on the UMC intranet for staff
- Lab time also arranged for a “test out” on care and insertion
- CAUTI Prevention incorporated into “Skills Fair” for floor specific competencies
Slide 79

Catheter Alternatives
- Began to reinforce use of catheter alternatives such as the condom catheter:
- Educate on proper application technique
- In-service on application of the Liberty condom Catheter
- Pilot use of the female urinal:
- Began a house-wide in-service on female urinal use after successful pilot on NSCU
- Well received by staff and patients
- Direct in-servicing provided to near 200 employees house-wide by NSCU’s CUSP team
- Posters developed with tips for incontinence care and available continence devices
Slide 80

Tips for Female Urinal Use
- Present the device to the patient; explain that it is a device to collect urine
- Assist the patient in placing the urinal flat side down, handle up between the patient’s legs flush to the perineum
- Adjust patient’s head to an upright position for comfort
Image: Photo of a female urinal.
Slide 81

Change in Stock of Catheter Trays
- Prior to project, both trays with a conventional drainage bag and urimeter trays were stocked in the ED & OR
- Often times, seal was being broken when pt received in ICU to place a temp sensing/urimeter drainage bag
- Skin Council & Supply collaborated to place urinary catheter trays in ED & OR to allow for more appropriate product placement
Slide 82

Getting the Students Involved
- Students are educated about On the CUSP: Stop CAUTI
- Students created CAUTI prevention display as their unit project
- Presented findings to staff and created care checklist for Foley care in patient rooms
- Staff took great pride collaborating with students and sharing knowledge
Image: Photo of a student produced display on preventing CAUTI.
Slide 83

Brags
- News of success house-wide:
- Presented at IC meetings
- Administrative support for continuing effort:
- Support for Nurse-Driven Removal Protocol
- Empowering staff to participate in activities beyond the bedside
- Opportunities to share our story with hospitals in the community:
- Keynote Presentation for Winter Plenary QIO Session
- Awards presented for NSCU’s work at Learning Session 3
- Article appearing in hospital newsletter The Pulse
- Participation in CDC sponsored “Reverse the Trend” Webinar
- Interview appearing in edition of APIC’s Prevention Strategist
Image: Photo of staff with awards.
Slide 84

Barriers
- Physician Buy-in
- Time & resources:
- Securing more commodes, finding times to meet, funding
- Staff schedule & availability:
- Low census, floating
- Competing Project Rollouts:
- EMR implementation
- Competing Project Rollouts
- Administrative Changes
- Fear about life without a Foley, “New Trick Anxiety”
Slide 85

How Are We Doing?
- Staff is advocating for Foley removal when not indicated
- Staff really taking ownership of CAUTI when occurring, reviewing what could be done
- Physicians on ICU Team assess for indication during daily rounds
- Catheter alternatives are used on a regular basis
- Infection Control reports less investigation of CAUTI incidents
- Foley Policy revised to reflect best practice including Nurse-driven Foley removal
- Plaques and articles displayed in the units
- Continuing to coordinate with Performance Improvement, Infection Control, Education, & other departments to reduce CAUTI
- Continuing to develop program to continue moving towards ZERO CAUTI
Slide 86

Thank you
Image: Photo of some UMC staff involved with On the CUSP.
Slide 87

Thank you!
Questions?
Slide 88

Funding
Prepared by the Health Research & Educational Trust of the American Hospital Association with contract funding provided by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality through the contract, “National Implementation of Comprehensive Unit-based Safety Program (CUSP) to Reduce Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI), project number HHSA290201000025I/HHSA29032001T, Task Order #1.”



