- Thirty years ago, the Heckler Report found that:
- Mortality statistics for the United States do not identify Hispanics separately, and until 1976, most other common measures of alcohol-related problems such as arrest and hospital discharge rates did not provide a Hispanic identifier. The 1979 National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism National Survey indicates that based on self-reported data, Hispanic American males age 18 and over have higher levels of heavy drinking and higher rates of alcohol-related problems than do nonminorities.
- Results from the 1983 single-room occupancy hotels study of drug abuse in New York City suggest that Hispanics have higher rates of drug use than Whites for marijuana, cocaine, heroin, and illicit methadone.
- Lung and esophageal cancer morbidity and mortality rates, known to be related to smoking, are lower for Hispanics than for Whites and Blacks.
Care for Substance Use Disorders for Hispanics
| Measure | Most Recent Disparity | Disparity Change |
|---|---|---|
| People age 12 and over who received any illicit drug or alcohol abuse treatment in the last 12 months | Same | No Change |
| People age 12 and over who needed treatment for illicit drug use or an alcohol problem and who received such treatment at a specialty facility in the last 12 months | Same | No Change |
| People age 12 and over treated for substance abuse who completed treatment course | Same | No Change |
- Trends: No measure of care for substance use disorders was improving for Hispanics.
- Groups With Disparities: Hispanics and Whites had similarly low rates of treatment for substance use disorders.
Substance Abuse Treatment
People age 12 and over who needed treatment for illicit drug use or an alcohol problem and who received such treatment at a specialty facility in the last 12 months, by race/ethnicity

| Race/Ethnicity | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 10.3 | 8.5 | 9.9 | 10.0 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 11.2 | 10.8 | 10.8 |
| White | 10.1 | 8.2 | 8.6 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 9.9 | 10.3 | 10.8 | 11.7 | 10.5 | 11.0 |
| Black | 15.3 | 13.1 | 17.3 | 18.4 | 14.2 | 18.2 | 13.2 | 14.7 | 12.8 | 14.3 | 12.7 |
| Hispanic | 7.4 | 6.4 | 9.7 | 11.7 | 14.3 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 10.2 | 8.1 |
2011 Achievable Benchmark: 15%.
Source: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2002-2012.
Denominator: Civilian noninstitutionalized population age 12 and over who needed treatment for illicit drug use or an alcohol problem.
Note: Treatment refers to treatment at a specialty facility, such as a drug and alcohol inpatient and/or outpatient rehabilitation facility, inpatient hospital setting, or mental health center.
- Overall Rate: In 2012, only 10.8% of people age 12 and over who needed treatment for illicit drug use or an alcohol problem received such treatment at a specialty facility in the last 12 months.
- Groups With Disparities: From 2002 to 2012, there were no statistically significant differences by race/ethnicity.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2011 top 6 State achievable benchmark was 15%. The top 6 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Alabama, Alaska, Delaware, Maryland, Oregon, and Utah.
- At the current rate, the total population would need 30 years to achieve this benchmark. Whites could achieve the benchmark in 15 years while Blacks and Hispanics are moving away from the benchmark.
Completion of Substance Abuse Treatment Course
People age 12 and over treated for substance abuse who completed treatment course, by race/ethnicity, 2005-2011, and by Hispanic group, 2011
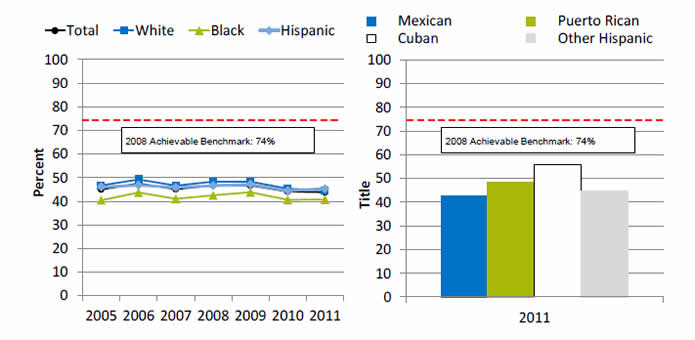
Left Graph:
| Race/Ethnicity | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 45.0 | 47.5 | 45.1 | 46.6 | 46.7 | 44.1 | 43.7 |
| Hispanic | 46.0 | 46.7 | 45.8 | 46.5 | 47.1 | 44.4 | 45.3 |
| White | 46.7 | 49.2 | 46.6 | 48.3 | 48.3 | 45.3 | 44.5 |
| Black | 40.4 | 43.6 | 41.0 | 42.5 | 43.8 | 40.6 | 40.7 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 74%.
Right Chart (Hispanic Group):
- Mexican - 42.8.
- Puerto Rican - 48.3.
- Cuban - 55.7.
- Other Hispanic - 44.8.
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 74%.
Source: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Treatment Episode Data Set, Discharge Data Set, 2005-2011.
Denominator: Discharges age 12 and over from publicly funded substance abuse treatment facilities.
- Overall Rate: In 2011, 43.7% of people age 12 and over treated for substance abuse completed their treatment course.
- Groups With Disparities:
- In 4 of 7 years, Blacks who were treated for substance abuse were significantly less likely than Whites to complete treatment.
- Hispanics and Whites had similar rates of treatment completion.
- In 2011, Cubans who were treated for substance abuse were significantly more likely than Whites to complete treatment.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 5 State achievable benchmark was 74%. The top 5 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Colorado, Connecticut, District of Columbia, Mississippi, and Texas.
- No group showed progress toward the benchmark.



