AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Hospital # ___________ Unit # ___________
Date (mm/dd/yyyy) ___________
| Fill out for all beds | Complete if patient is intubated or has tracheostomy and is mechanically ventilated | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bed # | Intub / Trach & Mech Vent | Date of Intubation (mm/dd/yyyy) |
SSD- ETT | SSD- ETT Contra | Location of Intub | HOB @ ≥30o | Hob Contra | Sedation Scale | ||
| RASS/ SAS/ Not Used in Unit | Target | Actual | ||||||||
| If RASS – 5 to 4, NS or X, NK | ||||||||||
| If SAS – 1 to 7, NS or X, NK | ||||||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
| Y N E | / / | Y N C | Y N C | RASS SAS NU | ||||||
Continued:
| Fill out for all beds | Complete if patient is intubated or has tracheostomy and is mechanically ventilated | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bed # | Intub / Trach & Mech Vent | Delirium Assessment | SAT | SAT Contra | SBT | SBT Contra | SBT With Seds Off? | |||
| CAM-ICU/ ASE/ ICDSC/ NU | CAM-ICU P, N, X, UTA, NK | ASE 0–10, X, UTA, NK | ICDSC P, N, X, UTA, NK | |||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
| Y N E | C A I NU | NS Y N C/NI | Y N C/NI | Y N NK | ||||||
C = Contraindicated; E = Empty; Intub = Intubation; Mech Vent = Mechanical Ventilation; N = Negative/No; NK = Not Known; NU = Not Used in this Unit; P = Positive; Trach = Tracheostomy; UTA = Unable to Assess; X = Not Performed; Y = Yes
Note: A glossary of additional acronyms can be found on the last page of this tool.
Contraindications and Locations
Select the appropriate number from below and enter it in the correct contraindications column above. If you have marked C or C/NI, indicate which contraindication is present.
| Subglottic Secretion Drainage Endotracheal Tube (SSD-ETT) Contraindications | Location of Intubation | Head of Bed (HOB) Contraindications |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Spontaneous Awakening Trial (SAT) Contraindications | Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT) Contraindications | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Instructions for Daily Care Processes Tool
Please complete this form once a day, every day. If possible, complete it around the same time each day, ideally during patient rounds.
Patients are considered mechanically ventilated on a specific day if they are mechanically ventilated at the time of observation.
All of the contraindications are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool. Print the data collection sheet with the contraindications on the back of the sheet for easier data collection.
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| Hospital | Enter the name of your hospital. |
| ICU | Enter the name of your unit. |
| Date | Enter today’s date as MM/DD/YYYY format (e.g. 01/31/2014). |
| Bed # | Enter all the bed numbers on the tool, whether the patient is on mechanical ventilation or not. Include empty beds. |
| Intub/Trach & Mech Vent: Is the patient currently receiving mechanical ventilation? | Enter for all patients. If the bed is empty, leave blank. Mechanical ventilation is defined as receiving ventilator support via an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube for the 24-hour day (except for SBT). Tracheostomy patients should be included starting at the time of positive pressure ventilation initiation.
|
| Date of Intubation: | Enter the date that the patient was intubated using MM/DD/YYYY format (e.g. 06/01/2012). Evaluate daily for patients receiving full vent support.
|
Subglottic Secretion Drainage Endotracheal Tubes
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| SSD-ETT: Does the patient have a subglottic secretion drainage endotracheal tube? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
|
| SSD-ETT Contra: Why is the use of a subglottic secretion drainage endotracheal tube contraindicated? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C entered in SSD-ETT. If C was entered in the SSD-ETT column, answer this question. Enter the number associated with the answer in the box. For example, enter 1 for tracheostomy. Contraindications are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool.
|
| Location of Intub: Where was the patient intubated? Patient must be extubated for 1 or more calendar days to consider this a new intubation. If patient is extubated for less than 1 calendar day, use the original location for subsequent data collection. |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving full ventilator support. Locations are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool.
|
Head of Bed
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| HOB @ ≥30°: Is the head of the bed at least 30 degrees from the horizontal position? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
|
| HOB Contra: Why is placing the head of the bed at an angle of 30 degrees or more, when compared to a horizontal surface, contraindicated? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving full ventilator support AND with C entered in the column labeled HOB @≥30°. If C was entered in the column labeled HOB @ ≥30°, answer this question. Enter the number associated with the answer into the box. For example, enter 1 for Hypotension. Contraindications are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool.
|
Sedation Scale
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| RASS/SAS/NU What sedation scale do you use on your unit? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
|
If you are a RASS or SAS user, please record the target and actual scores for RASS or SAS assessment closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score.
Evaluated daily for mechanically ventilated patients with R or S entered in the RASS/SAS/Not Used in This Unit column.
The Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Pain, Agitation, and Delirium (PAD) recommend the RASS and SAS as the most valid and reliable sedation assessment tools for measuring the quality and depth of sedation in adult ICU patients.
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| RASS: Target/Actual: What are the target and actual RASS scores for this patient? |
RASS (Only for patients receiving mechanical ventilation and where RASS/SAS/Not Used in This Unit = R) Enter the score closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score.
|
| SAS: Target/Actual: What are the target and actual SAS scores for this patient? |
SAS (Only for patients receiving mechanical ventilation and where RASS/SAS/Not Used in This Unit = S) Enter the score closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score.
|
Delirium Assessment
The Society of Critical Care Medicine’s Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management (SCCM) of Pain, Agitation, and Delirium (PAD) recommend the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU) or the Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC) as the most valid and reliable delirium screening tools, and that moderate- to high-risk patients be screened at least once per nursing shift.
ASE is the second step of the CAM-ICU. While it is not specifically recommended for use by the SCCM PAD Guidelines, it is a good tool to use while your unit is getting set up to do the full CAM-ICU. The results of the ASE may be abnormal due to disease, drugs, or other causes.
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| CAM-ICU/ ASE/ICDSC/NU What delirium assessment tool do you use in your unit? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
Note: If the use of the CAM-ICU is not yet feasible in your unit, we recommend that patients at least undergo the Attention Screening Exam (ASE) once daily. The ASE is feature 2 of the CAM-ICU, and this 10- to 20-second test of attention is the cardinal feature of a delirium diagnosis. |
If you are a CAM-ICU, ASE, or ICDSC user, please record the most recent CAM-ICU, ASE, or ICDSC assessment closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score. The CAM-ICU can be done while on or off sedation/analgesics and it is up to the clinical team to interpret the results of the delirium assessment in light of the presence or absence of sedatives/analgesics.
(Evaluated daily for patients with C, A, or I entered in the CAM-ICU/ASE/ICDSC/Not Used in This Unit column).
CAM-ICU
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| CAM-ICU: Is the patient positive or negative for delirium? |
(Only for patients receiving mechanical ventilation and where CAM-ICU/ASE/ICDSC/Not Used in This Unit = C) Enter the score closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score.
|
Attention Screening Exam (ASE)—Feature 2 of the CAM-ICU
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| ASE: What is the patient’s ability to pay attention? |
(Only for patients receiving mechanical ventilation and where CAM-ICU/ASE/ICDSC/Not Used in This Unit = A) The goal of this 10- to 20-second test is to determine if a patient can follow a simple command (pay attention) for that period of time. Inattention is the cardinal feature of delirium and must be present to diagnose delirium. For centers not using the full CAM-ICU or ICDSC, conducting the ASE is a good barometer of the presence or absence of delirium. This test may be abnormal due to disease, drugs, or other causes. The exam consists of the provider reading the following sequence of letters: S A V E A H A A R T or C A S A B L A N C A or A B A D B A D D A Y The patient is told to squeeze the provider’s hand when the letter A is stated. An error is defined as no squeeze with letter A or a squeeze on a letter other than A. The number of errors is counted. Inattention is present if the patient commits more than two errors. If the patient squeezes on every letter or doesn’t squeeze on any letter, then assign an error count of 10.Enter the score closest to 10 a.m. If two scores were collected equidistant from 10 a.m., choose the earlier score.
Note: If this is not yet feasible in your unit, we recommend that patients at least undergo the Attention Screening Exam (ASE) once daily. The ASE is feature 2 of the CAM-ICU and this 10- to 20-second test of attention is the cardinal feature of a delirium diagnosis. |
Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC)
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| ICDSC: Is the patient positive or negative for delirium? |
The ICDSC is an eight-item checklist of delirium symptoms evaluated over an 8- to 24-hour period. Patients are given one point for each symptom that manifests during the specified time frame (zero points if symptom did not manifest). The eight symptoms are: level of consciousness, inattention, disorientation, hallucinations/delusions/psychosis, psychomotor agitation or retardation, inappropriate speech or mood, sleep/wake cycle disturbances, and symptom fluctuation.
|
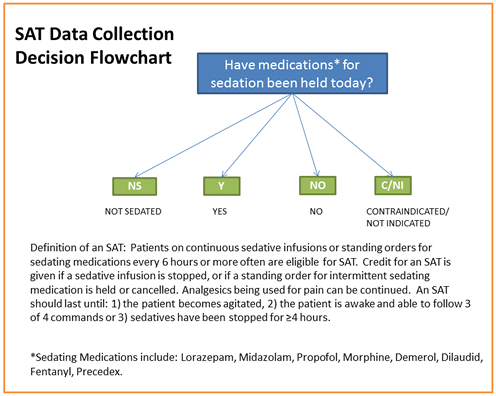
Spontaneous Awakening Trial (SAT)
Definition of an SAT: Patients on continuous sedative infusions or standing orders for sedating medications every 6 hours or more often are eligible for SAT. Credit for performing an SAT is given if a sedative infusion is stopped, or if a standing order for intermittent sedating medication is held or cancelled. Analgesics being used for pain can be continued.
An SAT should last until one of the following conditions occurs:
- Patient becomes agitated.
- Patient is awake and able to follow three of four commands.
- Sedatives have been stopped for at least 4 hours.
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| SAT: Has the patient had an SAT today? |
Evaluate every day for patients receiving mechanical ventilation. An overview of the decision process for the data collection portion of this measure is listed below. These are not the clinical procedures to be followed. SAT: Have medications for sedation been held today? (see flowchart below)
|
| SAT Contra: Why is an SAT inappropriate for this patient? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C/NI entered in the SAT column. If C/NI was entered in the SAT column, answer this question. Enter the number associated with the answer into the box. For example, enter 1 if patient is receiving sedatives for active seizures or has objective evidence of active alcohol withdrawal. Contraindications are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool.
|
Spontaneous Breathing Trial (SBT)
SBT definition: To conduct a trial of spontaneous breathing, ventilator support is removed and the patient is allowed to breathe through either a T-tube circuit or a ventilator circuit with low levels of pressure support (5–8 cm H2O in adults) with or without 5 cm H2O PEEP. No changes are required in the fraction of inspired oxygen or the level of PEEP.
| DATA FIELD | DIRECTIONS |
|---|---|
| SBT: Has the patient had an SBT today? |
Evaluated daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
|
| SBT Contra: Why is an SBT inappropriate for this patient? |
Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C entered in the SAT column. If C/NI was entered in the SBT column, answer this question. Enter the number associated with the answer into the box. Contraindications are listed on page 2 of the data collection tool.
|
| SBT With Seds Off: Was the SBT performed with the sedatives off? | Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with a Y entered in the SBT column.
|
Glossary of Acronyms
| ACRONYM | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| ASE | Attention Screening Exam |
| CAM-ICU | Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU |
| Contra | Contraindication |
| HOB | Head of bed |
| ICDSC | Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| RASS | Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale |
| SAS | Riker Sedation–Agitation Scale |
| SAT | Spontaneous awakening trial |
| SBT | Spontaneous breathing trial |
| Seds | Sedatives |
| SSD-ETT | Subglottic secretion drainage endotracheal tube |