National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report
Measures of Effective Treatment of Cancer
- Process:
- Women with clinical stage I-IIb breast cancer who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of surgery.
- Women under age 70 treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery who received radiation therapy to the breast within 1 year of diagnosis.
- Outcome:
- Age-adjusted breast cancer deaths per 100,000 population.
Measures of screening for cancer are located in the Healthy Living chartbook.
Cancer Measures for Which Disparities Were Eliminated
- Women under age 70 treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery who received radiation therapy to the breast within 1 year of diagnosis:
- White vs. Black.
- White vs. Asian.
Breast Cancer Treatment
Women With Breast Cancer Who Received Axillary Node Dissection or Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy at the Time of Surgery
Women with clinical Stage I-IIb breast cancer who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of lumpectomy or mastectomy, by residence location and race/ethnicity, 2004-2012
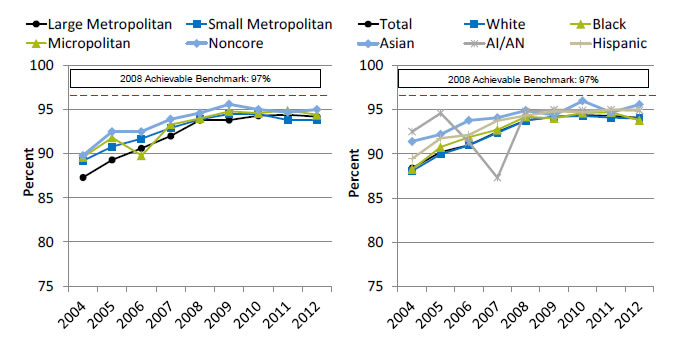
Left Chart:
| Location | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Large Metropolitan | 87.3 | 89.3 | 90.6 | 92.0 | 93.8 | 93.8 | 94.3 | 94.4 | 94.2 |
| Small Metropolitan | 89.2 | 90.8 | 91.7 | 92.9 | 93.9 | 94.5 | 94.5 | 93.8 | 93.8 |
| Micropolitan | 89.6 | 91.8 | 89.8 | 93.3 | 94.0 | 94.8 | 94.6 | 94.9 | 94.4 |
| Noncore | 89.8 | 92.5 | 92.5 | 93.9 | 94.6 | 95.6 | 95.0 | 94.7 | 95.0 |
Right Chart:
| Race/Ethnicity | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 88.4 | 90.2 | 91.0 | 92.5 | 93.8 | 94.2 | 94.4 | 94.3 | 94.1 |
| White | 88.1 | 90.0 | 91.0 | 92.4 | 93.8 | 94.2 | 94.3 | 94.1 | 94.0 |
| Black | 88.3 | 90.8 | 91.9 | 92.7 | 94.2 | 94.0 | 94.6 | 94.7 | 93.8 |
| Hispanic | 89.5 | 91.8 | 92.2 | 93.8 | 94.3 | 94.8 | 94.7 | 95.0 | 95.0 |
| AI/AN | 92.5 | 94.6 | 91.3 | 87.3 | 94.8 | 95.0 | 94.9 | 95.0 | 94.9 |
| Asian | 91.4 | 92.2 | 93.8 | 94.1 | 94.9 | 94.4 | 96.0 | 94.7 | 95.6 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 97%.
Key: AI/AN = American Indian or Alaska Native.
Source: Commission on Cancer, American College of Surgeons and American Cancer Society, National Cancer Data Base, 2004-2012.
Denominator: Women with breast cancer undergoing lumpectomy or mastectomy.
Note: White, Black, Asian, and AI/AN are non-Hispanic. Hispanic includes all races.
- Importance: Recommended cancer treatment depends on different factors, such as the stage or extent of the cancer within the body, especially whether the disease has spread from the original site to other parts of the body. If cancer cells have spread to the lymph nodes, there is a higher chance that the cells could have metastasized to other sites in the body. The more lymph nodes with breast cancer cells, the more likely it is that the cancer may be found in other organs as well. Therefore, finding cancer in one or more lymph nodes often affects the treatment plan.
- Trends: From 2004 to 2012, the percentage of women with clinical stage I-IIb breast cancer who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of lumpectomy or mastectomy improved overall and for all residence location and racial/ethnic groups except American Indians and Alaska Natives (AI/ANs).
- Groups With Disparities:
- In 7 of 9 years, the percentage of women who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy was higher for residents of noncore areas than for residents of large metropolitan areas.
- In 7 of 9 years, the percentage of women who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy was higher for Asian women than for White women.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 6 State achievable benchmark was 97%. The top 6 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Alaska, Arkansas, Nevada, Mississippi, Montana, and Oklahoma.
- At the current rates of improvement, the achievable benchmark could be attained overall in 4 years, in less than 6 years for all residence locations, and in less than 5 years for all racial/ethnic groups.
Women With Breast Cancer Who Received Axillary Node Dissection or Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy at the Time of Surgery, by Granular Ethnicities
Women with clinical Stage I-IIb breast cancer who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of lumpectomy or mastectomy, by granular Asian and Hispanic ethnicities, 2004-2012
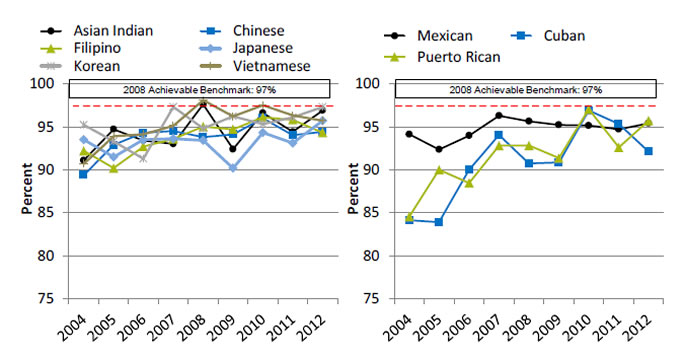
Left Chart:
| Ethnicity | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asian Indian | 91.1 | 94.7 | 93.4 | 93.0 | 97.6 | 92.4 | 96.6 | 94.4 | 96.9 |
| Chinese | 89.4 | 92.9 | 94.3 | 94.5 | 93.8 | 94.1 | 96.0 | 94.0 | 94.4 |
| Filipino | 92.2 | 90.2 | 92.7 | 93.6 | 95.0 | 94.7 | 96.1 | 95.8 | 94.3 |
| Japanese | 93.5 | 91.5 | 93.5 | 93.6 | 93.4 | 90.2 | 94.3 | 93.1 | 95.7 |
| Korean | 95.2 | 93.3 | 91.3 | 97.3 | 94.8 | 96.2 | 95.3 | 96.1 | 97.3 |
| Vietnamese | 90.7 | 93.9 | 94.1 | 95.1 | 98.1 | 96.2 | 97.5 | 96.3 | 95.7 |
Right Chart:
| Ethnicity | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mexican | 94.1 | 92.4 | 94.0 | 96.3 | 95.6 | 95.2 | 95.1 | 94.7 | 95.4 |
| Cuban | 84.1 | 83.9 | 90.0 | 94.0 | 90.7 | 90.9 | 96.9 | 95.3 | 92.1 |
| Puerto Rican | 84.6 | 90.0 | 88.5 | 92.8 | 92.8 | 91.4 | 97.0 | 92.6 | 95.7 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 97%.
Key: AI/AN = American Indian or Alaska Native.
Source: Commission on Cancer, American College of Surgeons and American Cancer Society, National Cancer Data Base, 2004-2012.
Denominator: Women with breast cancer undergoing lumpectomy or mastectomy.
Note: Puerto Ricans include patients receiving cancer care in hospitals in Puerto Rico.
- Importance: Asian and Hispanic groups are not homogeneous. Data on granular Asian and Hispanic ethnicities are limited but often show variation in care.
- Trends: From 2004 to 2012, the percentage of women with clinical stage I-IIb breast cancer who received axillary node dissection or sentinel lymph node biopsy at the time of lumpectomy or mastectomy improved for Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese, Cuban, and Puerto Rican women.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 6 State achievable benchmark was 97%. The top 6 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Alaska, Arkansas, Nevada, Mississippi, Montana, and Oklahoma.
- Koreans have achieved the benchmark.
- At the current rates of improvement, Asian Indian women will achieve the benchmark in less than 1 year, Puerto Ricans in 1 year, Vietnamese women in 2 years, Cubans in less than 4 years, Filipinos in less than 5 years, Chinese women in 6 years, and Mexicans and Japanese women in about 7 years.
Women Treated for Breast Cancer With Breast-Conserving Surgery Who Received Radiation Therapy
Women under age 70 treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery who received radiation therapy to the breast within 1 year of diagnosis, by race/ethnicity and residence location, 2004-2012
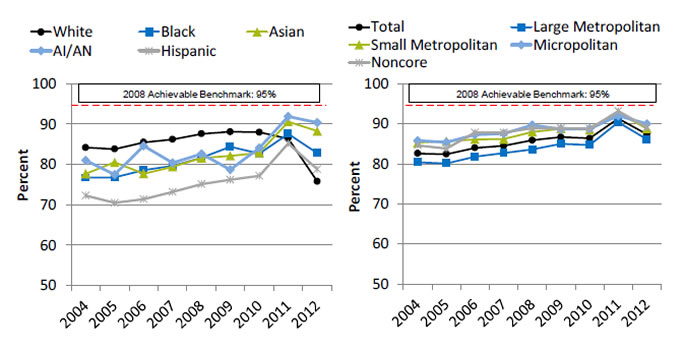
Left Chart:
| Year | White | Black | Hispanic | AI/AN | Asian |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 84.2 | 76.7 | 72.3 | 81 | 77.7 |
| 2005 | 83.8 | 76.8 | 70.5 | 77.5 | 80.5 |
| 2006 | 85.5 | 78.6 | 71.4 | 84.6 | 77.7 |
| 2007 | 86.2 | 79.6 | 73.2 | 80.4 | 79.4 |
| 2008 | 87.6 | 81.7 | 75.1 | 82.6 | 81.6 |
| 2009 | 88.1 | 84.4 | 76.2 | 78.7 | 82.1 |
| 2010 | 88 | 82.7 | 77.2 | 84.1 | 82.9 |
| 2011 | 86.4 | 87.6 | 85.2 | 91.9 | 90.6 |
| 2012 | 75.8 | 82.8 | 78.8 | 90.4 | 88.3 |
Right Chart:
| Year | Total | Large Metropolitan | Small Metropolitan | Micropolitan | Noncore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 82.6 | 80.4 | 85.3 | 85.8 | 84.6 |
| 2005 | 82.4 | 80.1 | 85.7 | 85.4 | 83.8 |
| 2006 | 84 | 81.8 | 86.1 | 87.3 | 87.8 |
| 2007 | 84.5 | 82.7 | 86.2 | 87.6 | 87.8 |
| 2008 | 85.9 | 83.6 | 88 | 89.7 | 88.9 |
| 2009 | 86.7 | 85 | 88.8 | 88.7 | 88.9 |
| 2010 | 86.4 | 84.7 | 88.5 | 88.8 | 88.8 |
| 2011 | 91.3 | 90.4 | 92.7 | 92 | 93.2 |
| 2012 | 87.4 | 86.1 | 88.8 | 90 | 89.1 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 95%.
Key: AI/AN = American Indian or Alaska Native.
Source: Commission on Cancer, American College of Surgeons and American Cancer Society, National Cancer Data Base, 2004-2012.
Denominator: Women with breast cancer undergoing breast-conserving surgery.
- Importance: Radiotherapy decreases local recurrence rates and improves outcomes for women with invasive breast cancer who undergo breast-conserving surgery. For breast-conserving surgery patients younger than 70 years, delivery of radiotherapy within 1 year is a Commission on Cancer quality-of-cancer-care measure with an expected compliance rate of 90% or more (Hieken, et al., 2016).
- Trends: From 2004 to 2012, the percentage of women treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery who received radiation therapy improved overall and for all racial/ethnic groups except Whites and for all residence locations.
- Groups With Disparities:
- In 7 of 9 years, Black, Asian, and Hispanic women who were treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery were less likely than White women to receive radiation therapy.
- In all years, residents of small metropolitan, micropolitan, and noncore areas who were treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery were more likely than residents of large metropolitan areas to receive radiation therapy.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 5 State achievable benchmark was 95%. The top 5 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Kansas, Minnesota, Montana, New Hampshire, and Wisconsin.
- At the current rates of improvement, Asian and AI/AN women could achieve the benchmark in less than 5 years.
- Hispanic and Black women could achieve the benchmark in about 11 years.
- White women are making no progress toward the benchmark.
Women Treated for Breast Cancer With Breast-Conserving Surgery Who Received Radiation Therapy, by Granular Ethnicities
Women under age 70 treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery who received radiation therapy to the breast within 1 year of diagnosis, by granular Asian and Hispanic ethnicities, 2004-2012
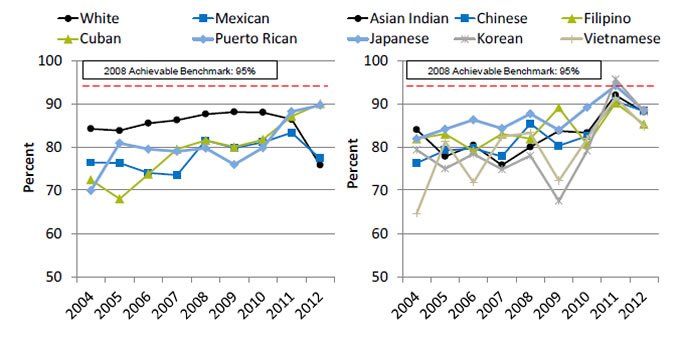
Left Chart:
| Year | White | Mexican | Cuban | Puerto Rican |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 84.2 | 76.4 | 72.4 | 69.9 |
| 2005 | 83.8 | 76.3 | 68 | 80.9 |
| 2006 | 85.5 | 74 | 73.7 | 79.5 |
| 2007 | 86.2 | 73.5 | 79.5 | 79 |
| 2008 | 87.6 | 81.5 | 81.5 | 79.7 |
| 2009 | 88.1 | 79.8 | 80 | 75.9 |
| 2010 | 88 | 81.1 | 81.7 | 79.8 |
| 2011 | 86.4 | 83.3 | 87.1 | 88.2 |
| 2012 | 75.8 | 77.3 | 90 | 89.7 |
Right Chart:
| Year | Asian Indian | Chinese | Filipino | Japanese | Korean | Vietnamese |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 84 | 76.3 | 81.9 | 81.9 | 79.3 | 64.6 |
| 2005 | 77.8 | 79.2 | 83 | 84.1 | 75 | 81.3 |
| 2006 | 80.4 | 79.7 | 79.1 | 86.3 | 78.4 | 71.8 |
| 2007 | 75.8 | 77.8 | 83 | 84.3 | 74.8 | 82.4 |
| 2008 | 80 | 85.4 | 81.9 | 87.7 | 78 | 83.3 |
| 2009 | 83.7 | 80.3 | 89.1 | 83.9 | 67.5 | 72.2 |
| 2010 | 83.3 | 82.5 | 80.6 | 89.2 | 79.1 | 81.9 |
| 2011 | 92 | 90.6 | 90.2 | 94.2 | 95.7 | 91.4 |
| 2012 | 88.1 | 88.3 | 85.3 | 88.5 | 88.2 | 84.8 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 95%.
Source: Commission on Cancer, American College of Surgeons and American Cancer Society, National Cancer Data Base, 2004-2012.
Denominator: Women with breast cancer undergoing breast-conserving surgery.
- Importance: Breast-conserving surgery followed by radiation therapy is an established standard of care for early stage breast cancer with equivalent survival for invasive breast cancer patients compared with mastectomy. Minority women with early stage breast cancer have been reported to have double the risk for failing to receive necessary adjuvant treatments compared with White women (Parise, et al., 2012).
- Groups With Disparities:
- In 7 of 9 years, Mexican women who were treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery were less likely than White women to receive radiation therapy.
- In 2012, Cuban, Puerto Rican, Asian Indian, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean women who were treated for breast cancer with breast-conserving surgery were more likely than White women to receive radiation therapy.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 5 State achievable benchmark was 95%. The top 5 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Kansas, Minnesota, Montana, New Hampshire and Wisconsin.
- At the current rates of improvement, Cubans could reach the benchmark in 2 years, Puerto Ricans in 3 years but it would take Mexican women nearly 24 years to achieve the benchmark.
- Korean women achieved the benchmark in 2011.
- At the current rates of improvement, Chinese women could achieve the benchmark in 2.5 years, Vietnamese in 5 years, Asian Indians and Japanese in about 6 years and Filipinos in 13 years.
Breast Cancer Deaths
Age-Adjusted Breast Cancer Deaths
Age-adjusted breast cancer deaths per 100,000 female population, by race/ethnicity and geographic location, 2004-2013
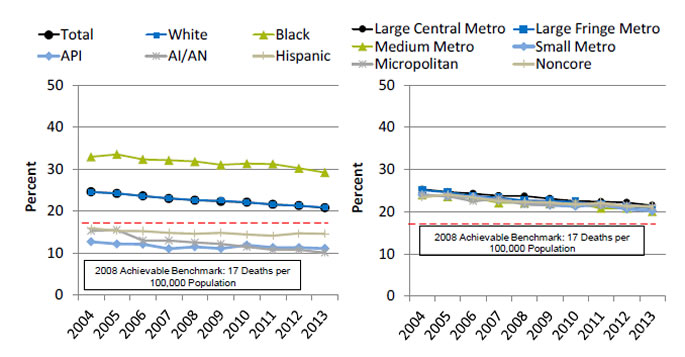
Left Chart:
| Race/Ethnicity | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 24.6 | 24.2 | 23.6 | 23 | 22.6 | 22.3 | 22.1 | 21.6 | 21.3 | 20.8 |
| White | 24.6 | 24.2 | 23.6 | 23.1 | 22.6 | 22.5 | 22.1 | 21.6 | 21.3 | 20.9 |
| Black | 32.9 | 33.5 | 32.3 | 32.1 | 31.8 | 31 | 31.3 | 31.2 | 30.2 | 29.2 |
| Hispanic | 15.9 | 15.3 | 15.2 | 14.8 | 14.6 | 14.8 | 14.4 | 14.1 | 14.7 | 14.6 |
| AI/AN | 15.3 | 15.5 | 13.0 | 13 | 12.5 | 12.2 | 11.5 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.1 |
| API | 12.7 | 12.2 | 12.1 | 11 | 11.5 | 11.1 | 11.9 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 11.1 |
Right Chart:
| Year | Large Central Metro | Large Fringe Metro | Medium Metro | Small Metro | Micropolitan | Noncore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | 25.3 | 25.1 | 24 | 24 | 24 | 23.4 |
| 2005 | 24.7 | 24.6 | 23.6 | 23.7 | 23.7 | 24.1 |
| 2006 | 24.3 | 23.7 | 23.3 | 23.5 | 22.5 | 23.4 |
| 2007 | 23.8 | 23.3 | 22.1 | 22.8 | 23.1 | 22.5 |
| 2008 | 23.7 | 22.7 | 22.1 | 22 | 21.7 | 22.3 |
| 2009 | 23.1 | 22.6 | 21.9 | 21.5 | 21.6 | 22.2 |
| 2010 | 22.5 | 22.3 | 22 | 21.3 | 22 | 21.7 |
| 2011 | 22.4 | 21.7 | 20.8 | 21.7 | 21.5 | 22.1 |
| 2012 | 22.2 | 21.2 | 20.8 | 20.6 | 21.5 | 21.3 |
| 2013 | 21.5 | 20.8 | 20 | 20.2 | 21.1 | 21.3 |
2008 Achievable Benchmark: 17 Deaths per 100,000 Population.
Key: API = Asian or Pacific Islander; AI/AN = American Indian or Alaska Native.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System—Mortality, 2004-2013.
Denominator: U.S. population.
Note: For this measure, lower rates are better. Total rate is age adjusted to the 2000 U.S. standard population.
- Importance: The death rate from a disease is a function of many factors, including the causes of the disease; social forces; and effectiveness of the health care system in providing prevention, treatment, and management of the disease. Breast cancer deaths reflect the impact of breast cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Trends: From 2004 to 2013, the age-adjusted breast cancer death rate improved overall and for all racial/ethnic groups and geographic locations.
- Groups With Disparities:
- In all years, the breast cancer death rate was lower for Asian and Pacific Islander (API), AI/AN, and Hispanic females than for White females.
- In all years, the breast cancer death rate was higher for Black females than for White females.
- Achievable Benchmark:
- The 2008 top 5 State achievable benchmark was 17 deaths per 100,000 population. The top 5 States that contributed to the achievable benchmark are Alaska, Hawaii, Montana, Vermont, and Wyoming.
- The benchmark has been achieved by API, AI/AN, and Hispanic females.
- At the current rates of improvement, the achievable benchmark could be attained overall and for Whites in 9 years but Blacks would require 30 years.
References
Hieken TJ, Mutter RW, Jakub JW, et al. A novel treatment schedule for rapid completion of surgery and radiation in early-stage breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2016 Jun 22 [Epub ahead of print].
Parise CA, Bauer KR, Caggiano V. Disparities in receipt of adjuvant radiation therapy after breast-conserving surgery among the cancer-reporting regions of California. Cancer 2012;118:2516-24. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/cncr.26542/full. Accessed August 29, 2016.



