|
Overview |
Definition of Sustainability and its Importance in Quality Improvement
|
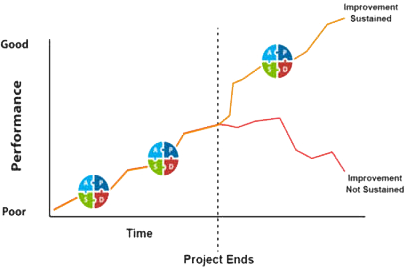
Image: The graph shows how as a project ends, the gains can be sustained or not sustained, and is contingent on continuous PDSA and monitoring.
15-Minute Meeting Suggested Activities
Toolkit materials are designed to be modified and customized. Here are suggestions for time-conscious ways to use this module. Feel free to use these suggestions or come up with your own approach to implementing the module.
Topic: Definition of Sustainability and its Importance in Quality Improvement
Method: In a meeting, discuss what sustainability means for your quality improvement project(s), whether your project(s) are sustainable, and why sustainability is important. Present slides 4-12 and lead a discussion comparing definitions and explaining why sustainability starts early in the improvement planning process to ensure success. Compare differences between sustainability and spread and how they can overlap.
Materials: Slides 4-12
Audience: All employees, especially administrators, managers, and project leads
Topic: Barriers and Solutions to Sustaining Improvements
Method: Hand out slides 13-17 and facilitator notes at beginning of meeting. Have staff review barriers to sustainability and select which are barriers within your facility. Discuss team resistance to change and identify solutions to reduce resistance and help the project sustain its gains.
Materials: Slides 13-17
Audience: Administrators, managers, and project leads
Topic: Steps to Creating and Implementing a Sustainability Plan
Method: Present slides 18-24 in a meeting using the facilitator notes. Facilitate a discussion of what steps the facility can take to support a team leading the program’s process changes in such a way that they become embedded into work done every day. Listen to the recordings in slides 23 and 24 and invite the staff to talk about the main messages. Talk about recognition and rewards that would be meaningful to the staff when data reveals improvement goals are met.
Materials: Slides 18-24, Engaging Staff with Stories audio, Recognizing and Celebrating Success audio
Audience: All employees, especially administrators, managers, and project leads
Topic: Establishing a Sustainability Measurement Plan
Method: Present slides 25-38 lecture style with facilitator notes. Discuss how the required data will be collected (slide 28) and what data will measure the new work processes (slide 32). Set outcome goals and decide what will be done if the data reveal a threshold of safety has been passed. Design a communication system to share the data results with others (e.g., board, frontline staff) to engage staff in sustainability using feedback and progress reports.
Materials: Slides 25-38
Audience: Administrators, nurse leader, medical director, and frontline staff
Topic: Learn From Sustainability Examples
Method: Use slides 36-38 to assist staff in brainstorming discussions of how to plan, implement, and evaluate their sustainability plan and to identify gaps that may lessen the effectiveness of their plan.
Materials: Slides 36-38
Audience: Administrator, nurse leader, medical director, and frontline staff



