Measure Descriptions for Daily Care Processes: Slide Presentation
AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Slide 1: AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients

Measure Descriptions for Daily Care Processes
Slide 2: Learning Objectives

After this session, you will be able to—
- Collect and enter Daily Care Process (DCP) data using the DCP data collection tool.
- Understand the definitions of the data elements.
- Locate the necessary data elements.
Slide 3: Daily Care Processes: Key Interventions
- Use a subglottic secretion drainage endotracheal tube (SSD-ETT) for patients intubated for more than 72 hours.
- Elevate the head of bed (HOB) to at least 30 degrees.
- Interrupt sedation daily and minimize sedative use.
- Assess sedation and delirium with structured scales.
- Perform spontaneous awakening trials (SAT) and spontaneous breathing trials (SBT).
Slide 4: Data Collection

- Drives quality improvement efforts.
- Can be used for quality improvement processes or for research.
- Provides quantifiable measures of care practices.
- Guides patient safety conversations.
- Justifies resource allocations:
- Human resources (time).
- Financial resources (money).
- Supplies and equipment (stuff).
Slide 5: Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool
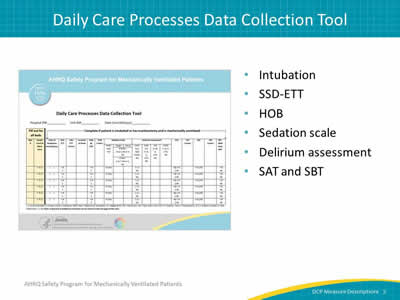
Image: The AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients Daily Care Data Collection Tool is shown with the text:
- Intubation.
- SSD-ETT.
- HOB.
- Sedation scale.
- Delirium assessment.
- SAT and SBT.
Slide 6: Data Collection: Intubation, SDD-ETT, and HOB
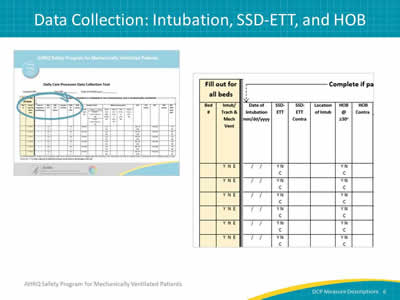
Image: The AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool is shown as well as a closeup of the intubation, SSD-ETT, and HOB columns of the Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool.
Slide 7: Let's Begin…

Image: The AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool is shown with the following text:
Fill out for all beds:
- Track by bed, not by patient.
- Include:
- Bed number.
- Was the patient in that bed intubated or trached AND on mechanical ventilation at the time of observation?
- Y = Yes
- N = No
- E = Empty bed
Slide 8: Date of Intubation
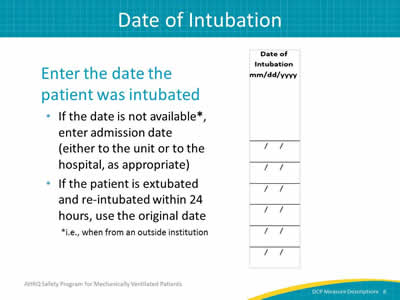
Image: Detail of the date of intubation column of the Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool.
Enter the date the patient was intubated:
- If the date is not available*, enter admission date (either to the unit or to the hospital, as appropriate).
- If the patient is extubated and re-intubated within 24 hours, use the original date.
*i.e., when from an outside institution
Slide 9: SSD-ETT
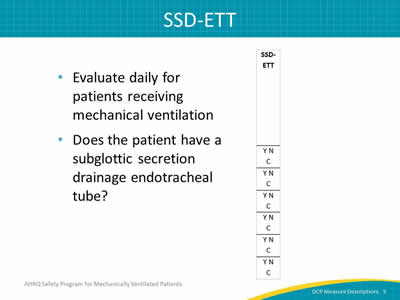
Image: Detail of the SSD-ETT column.
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation
- Does the patient have a subglottic secretion drainage endotracheal tube?
Slide 10: SSD-ETT
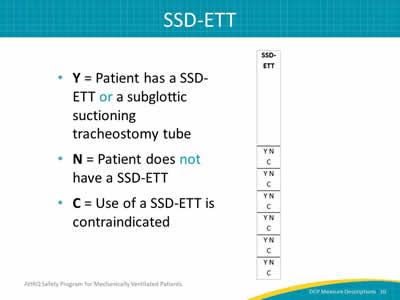
Image: Detail of SSD-ETT column.
- Y = Patient has a SSD-ETT or a subglottic suctioning tracheostomy tube.
- N = Patient does not have a SSD-ETT.
- C = Use of a SSD-ETT is contraindicated.
Slide 11: SSD-ETT Contraindications
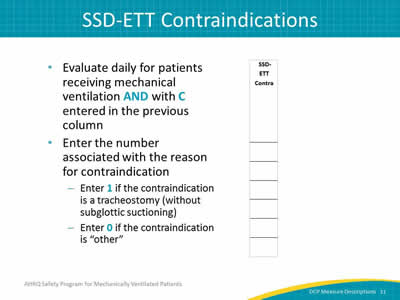
Image: Detail of SSD-ETT Contra column.
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C entered in the previous column.
- Enter the number associated with the reason for contraindication:
- Enter 1 if the contraindication is a tracheostomy (without subglottic suctioning).
- Enter 0 if the contraindication is "other."
Slide 12: Location of Intubation
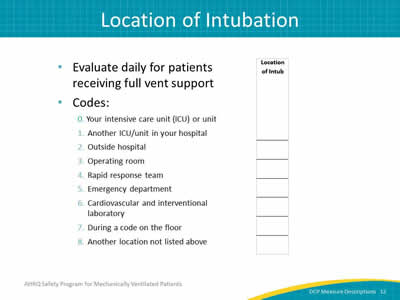
Image: Detail of the location of intubation column.
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving full vent support.
- Codes:
0. Your intensive care unit (ICU) or unit.
1. Another ICU/unit in your hospital.
2. Outside hospital.
3. Operating room.
4. Rapid response team.
5. Emergency department.
6. Cardiovascular and interventional laboratory.
7. During a code on the floor.
8. Another location not listed above.
Slide 13: HOB ≥ 30 Degrees
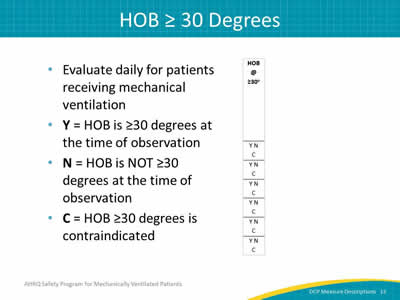
Image: Detail of HOB column.
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
- Y = HOB is ≥30 degrees at the time of observation.
- N = HOB is NOT ≥30 degrees at the time of observation.
- C = HOB ≥30 degrees is contraindicated.
Slide 14: HOB Elevation Contraindications
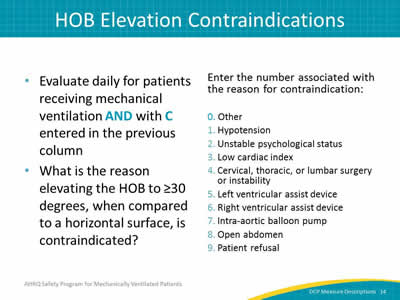
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C entered in the previous column.
- What is the reason elevating the HOB to ≥30 degrees, when compared to a horizontal surface, is contraindicated?
Enter the number associated with the reason for contraindication:
0. Other.
1. Hypotension.
2. Unstable psychological status.
3. Low cardiac index.
4. Cervical, thoracic, or lumbar surgery or instability.
5. Left ventricular assist device.
6. Right ventricular assist device.
7. Intraaortic balloon pump.
8. Open abdomen.
9. Patient refusal.
Slide 15: Data Collection: Sedation and Delirium
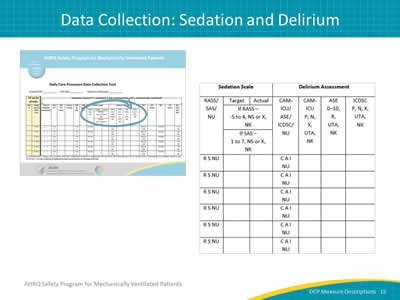
Image: The sedation scale and delirium assessment columns.
Slide 16: Sedation Scale
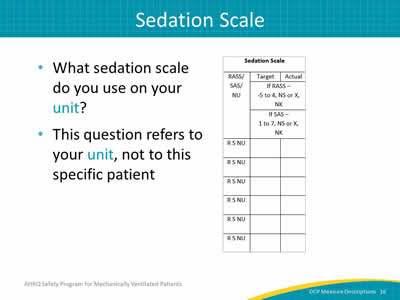
Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
- What sedation scale do you use on your unit?
- This question refers to your unit, not to this specific patient.
Slide 17: Sedation Scale
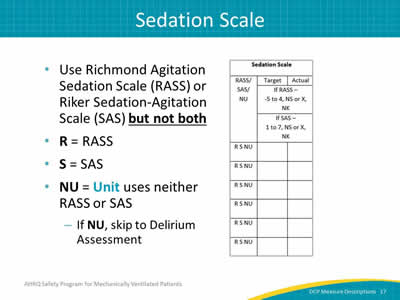
Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
- Use Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS) or Riker Sedation-Agitation Scale (SAS) but not both.
- R = RASS.
- S = SAS.
- NU = Unit uses neither RASS or SAS.
- If NU, skip to Delirium Assessment.
Slide 18: Sedation Scale: Target RASS
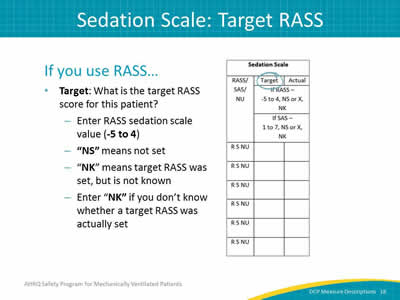
Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
If you use RASS…
- Target: What is the target RASS score for this patient?
- Enter RASS sedation scale value (-5 to 4).
- "NS" means not set.
- "NK" means target RASS was set, but is not known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether a target RASS was actually set.
Slide 19: Sedation Scale: Actual RASS

Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
If you use RASS…
- Actual: What is the actual RASS score for this patient?
- Enter RASS sedation scale value (-5 to 4).
- Enter "X" if an actual RASS sedation level was not scored.
- Enter "NK" if target RASS was scored, but is not known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether a target RASS was actually scored.
Slide 20: Sedation Scale: Target SAS

Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
If you use SAS…
- Target: What is the target SAS score for this patient?
- Enter SAS sedation scale value (1 to 7).
- Enter "NS" if not set.
- Enter "NK" if target SAS was set but is not known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether a target SAS was actually set.
Slide 21: Sedation Scale: Actual SAS
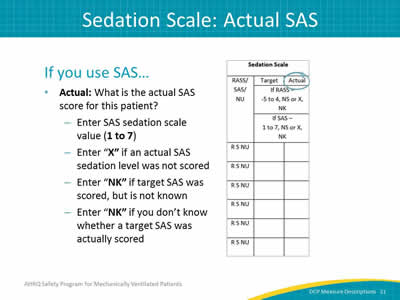
Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
If you use SAS…
- Actual: What is the actual SAS score for this patient?
- Enter SAS sedation scale value (1 to 7).
- Enter "X" if an actual SAS sedation level was not scored.
- Enter "NK" if target SAS was scored, but is not known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether a target SAS was actually scored.
Slide 22: Sedation Scale: NU
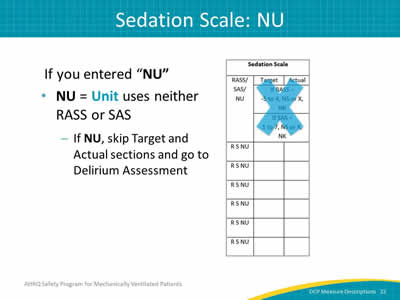
Image: Detail of the sedation scale column.
If you entered "NU":
- NU = Unit uses neither RASS or SAS.
- If NU, skip Target and Actual sections and go to Delirium Assessment.
Slide 23: Delirium Assessment

Society of Critical Care Medicine’s 2013 Pain, Agitation, and Delirium (PAD) clinical practice guidelines:
- Recommends theses valid and reliable delirium screening tools:
- Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU).
- Intensive Care Delirium Screening Checklist (ICDSC).
- Screen moderate to high risk patients at least once per nursing shift.
Slide 24: Delirium Assessment
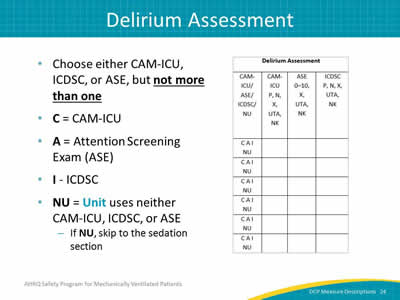
Image: Detail of the delirium assessment column.
- Choose either CAM-ICU, ICDSC, or ASE, but not more than one.
- C = CAM-ICU.
- A = Attention Screening Exam (ASE).
- I - ICDSC.
- NU = Unit uses neither CAM-ICU, ICDSC, or ASE:
- If NU, skip to the sedation section.
Slide 25: Delirium Assessment: CAM-ICU
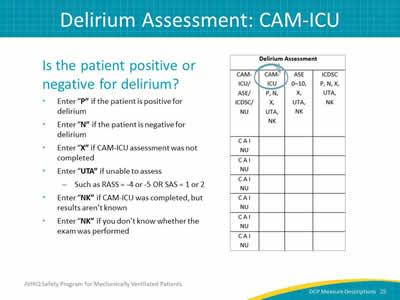
Image: Detail of the delirium assessment column
Is the patient positive or negative for delirium?
- Enter "P" if the patient is positive for delirium.
- Enter "N" if the patient is negative for delirium.
- Enter "X" if CAM-ICU assessment was not completed.
- Enter "UTA" if unable to assess:
- Such as RASS = -4 or -5 OR SAS = 1 or 2.
- Enter "NK" if CAM-ICU was completed, but results aren’t known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether the exam was performed.
Slide 26: Delirium Assessment: ICDSC
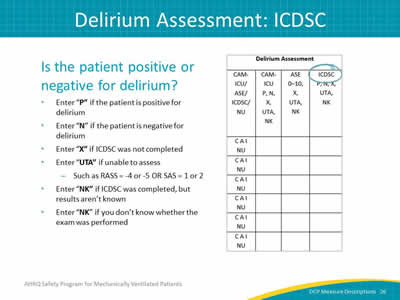
Image: Detail of the delirium assessment column.
Is the patient positive or negative for delirium?
- Enter "P" if the patient is positive for delirium.
- Enter "N" if the patient is negative for delirium.
- Enter "X" if CAM-ICU assessment was not completed.
- Enter "UTA" if unable to assess:
- Such as RASS = -4 or -5 OR SAS = 1 or 2.
- Enter "NK" if CAM-ICU was completed, but results aren’t known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether the exam was performed.
Slide 27: Delirium Assessment: Attention Screening Exam
If the CAM-ICU or ICDSC are not yet feasible in your unit—
- Second feature of the CAM-ICU.
- 10- to 20-second test.
- Goal to determine if patient can follow a simple command for that period of time.
- Inattention must be present to diagnose delirium.
- Recommend patients at least undergo the ASE once per nursing shift.
- Recognize that ASE may be abnormal due to disease, drugs, or other causes.
Slide 28: Attention Screening Exam

- Provider reads one of the following sequences:
- S A V E A H A A R T
- C A S A B L A N C A
- A B A D B A D D A Y
- Patient squeezes the provider’s hand when he hears the letter "A".
- Error defined as—
- No squeeze with letter "A".
- A squeeze on a letter other than "A".
Slide 29: Attention Screening Exam

- Count the number of errors.
- Inattention is present if the patient commits more than two errors.
- If the patient squeezes on every letter, assign an error count of 10.
- If the patient doesn’t squeeze on any letter, assign an error count of 10.
Slide 30: Attention Screening Exam
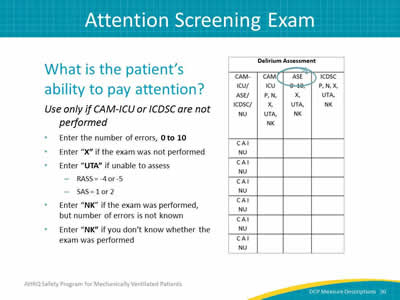
Image: Detail of the delirium assessment column.
What is the patient’s ability to pay attention?
Use only if CAM-ICU or ICDSC are not performed.
- Enter the number of errors, 0 to 10.
- Enter "X" if the exam was not performed.
- Enter "UTA" if unable to assess:
- RASS = -4 or -5.
- SAS = 1 or 2.
- Enter "NK" if the exam was performed, but number of errors is not known.
- Enter "NK" if you don’t know whether the exam was performed.
Slide 31: Data Collection: SAT and SBT
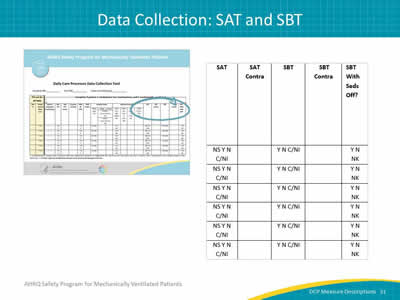
Images: The AHRQ Safety Program for Mechanically Ventilated Patients Daily Care Processes Data Collection Tool are shown with the SAT and SBT columns from data collection tool.
Slide 32: Spontaneous Awaking Trial
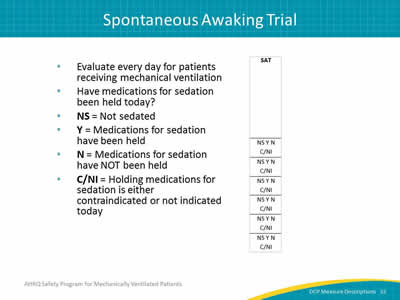
Image: Detail of SAT column.
- Evaluate every day for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
- Have medications for sedation been held today?
- NS = Not sedated.
- Y = Medications for sedation have been held.
- N = Medications for sedation have NOT been held.
- C/NI = Holding medications for sedation is either contraindicated or not indicated today.
Slide 33: SAT—Contraindications
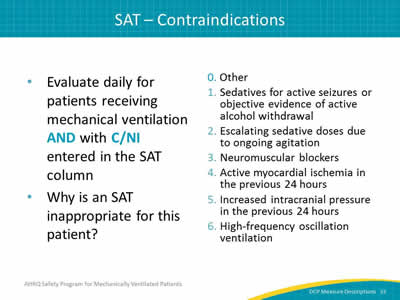
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C/NI entered in the SAT column.
- Why is an SAT inappropriate for this patient?
0. Other.
1. Sedatives for active seizures or objective evidence of active alcohol withdrawal.
2. Escalating sedative doses due to ongoing agitation.
3. Neuromuscular blockers.
4. Active myocardial ischemia in the previous 24 hours.
5. Increased intracranial pressure in the previous 24 hours.
6. High-frequency oscillation ventilation.
Slide 34: Spontaneous Breathing Trial
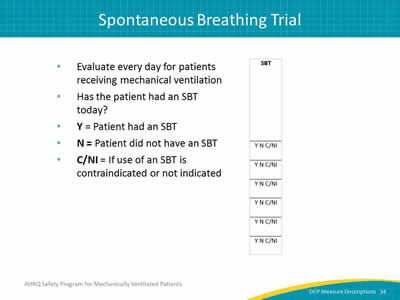
Image: Detail of SBT column.
- Evaluate every day for patients receiving mechanical ventilation.
- Has the patient had an SBT today?
- Y = Patient had an SBT.
- N = Patient did not have an SBT.
- C/NI = If use of an SBT is contraindicated or not indicated.
Slide 35: SBT—Contraindications
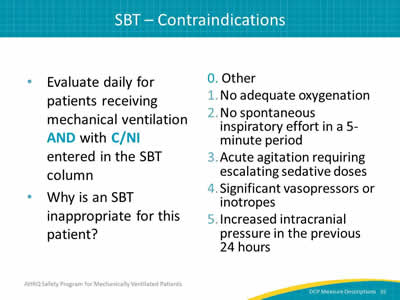
- Evaluate daily for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with C/NI entered in the SBT column.
- Why is an SBT inappropriate for this patient?
0. Other.
1. No adequate oxygenation.
2. No spontaneous inspiratory effort in a 5-minute period.
3. Acute agitation requiring escalating sedative doses.
4. Significant vasopressors or inotropes.
5. Increased intracranial pressure in the previous 24 hours.
Slide 36: SBT—With Sedatives Off
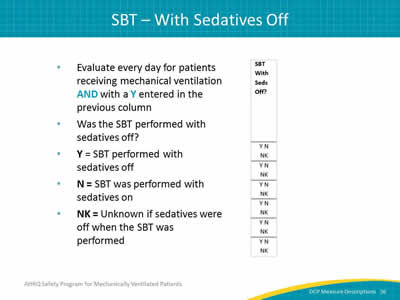
Image: Detail of SBT with seds off column.
- Evaluate every day for patients receiving mechanical ventilation AND with a Y entered in the previous column.
- Was the SBT performed with sedatives off?
- Y = SBT performed with sedatives off.
- N = SBT was performed with sedatives on.
- NK = Unknown if sedatives were off when the SBT was performed.
Slide 37: Data Measures Guide
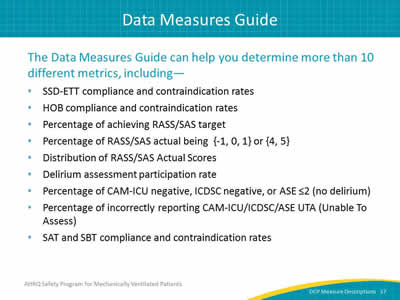
The Data Measures Guide can help you determine over 10 different metrics, including—
- SSD-ETT compliance and contraindication rates.
- HOB compliance and contraindication rates.
- Percentage of achieving RASS/SAS target.
- Percentage of RASS/SAS actual being {-1, 0, 1} or {4, 5}.
- Distribution of RASS/SAS Actual Scores.
- Delirium assessment participation rate.
- Percentage of CAM-ICU negative, ICDSC negative, or ASE ≤2 (no delirium).
- Percentage of incorrectly reporting CAM-ICU/ICDSC/ASE UTA (Unable To Assess).
- SAT and SBT compliance and contraindication rates.
Slide 38: Data Measures Guide

Data should drive all quality improvement efforts…
The Data Measures Guide provides detailed instructions on how to calculate and evaluate process and outcome measures in your unit using data gathered from the data collection tools provided for this safety program. The guide can be found on the AHRQ Web site at www.ahrq.gov/HAImvp.
Slide 39: Questions?

Image: A series of question marks meant to evoke questions from the audience.



